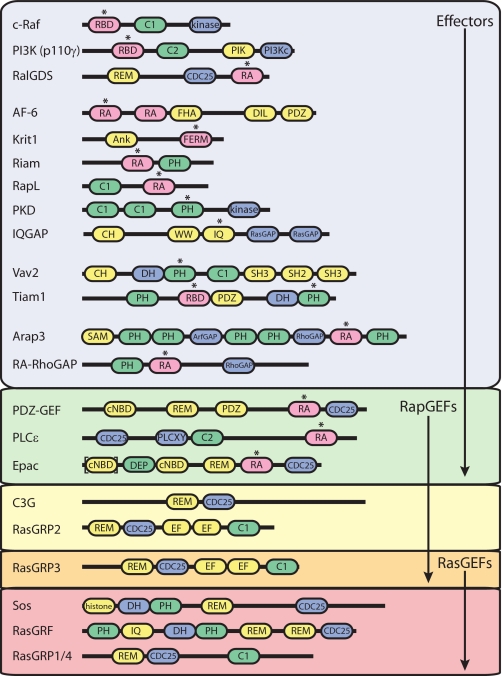
FIGURE 1.
Ras and Rap effector proteins and GEFs. A schematic representation is shown of the domain structures of Ras and Rap GEFs and effector proteins discussed here. RA domains/RBDs are depicted in pink, catalytic domains in blue, lipid-binding domains in green, and other domains in yellow. Asterisks indicate domains required for Ras/Rap binding. C1, protein kinase C conserved region 1; C2, Ca2+-binding motif; PIK, PI3K accessory domain; PI3Kc, PI3K catalytic domain; CDC25, CDC25 homology; FHA, Forkhead-associated domain; DIL, dilute; Ank, ankyrin repeat; CH, calponin homology; SAM, sterile α-motif; cNBD, cyclic nucleotide-binding domain; PLCXY, phospholipase C catalytic regions X and Y; DEP, Dishevelled/Egl-10/pleckstrin; EF, EF-hand; histone, histone domain. 1) The interaction of Tiam1 with Ras has been described for the RBD; for Rap, it was shown to bind to the DH-PH domain. 2) The N-terminal cyclic nucleotide-binding domain is conserved in Epac2 alone, and the RA domain-like sequence in Epac1 is not recognized as such by the SMART Database (smart.embl-heidelberg.de). 3) Although described to be present in PLCε (18, 45), a second RA domain in PLCε is not indicated in the SMART Database.