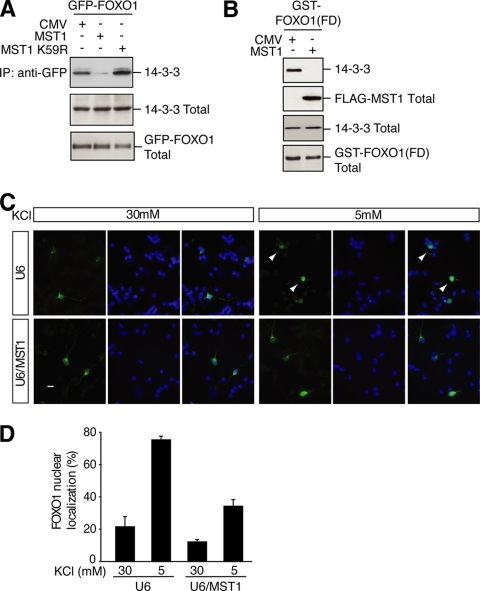
FIGURE 3.
MST1-induced phosphorylation of FOXO1 disrupts FOXO1's interaction with 14-3-3 proteins and promotes the nuclear accumulation of FOXO1. A, lysates of 293T cells transfected with the GFP-FOXO1 expression plasmid together with an expression vector encoding FLAG-MST1, FLAG-MST1 K59R, or the control vector were immunoprecipitated (IP) with the GFP antibody followed by immunoblotting with a 14-3-3 antibody (top panel). The total 14-3-3 and GFP-FOXO is shown in the middle and lower panels. MST1, but not the kinase-dead MST1 K59R, disrupted FOXO1's interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. CMV, cytomegalovirus. B, lysates of 293T cells transfected with a mammalian expression vector encoding GST-FOXO1(FD) together with the MST1 expression plasmid or its control vector were subjected to GST pull-down assays followed by immunoblotting with the 14-3-3 antibody (top panel). The total MST1, 14-3-3, and FOXO1(FD) is shown in the lower panels. C, granule neurons transfected with GFP-FOXO1 together with the MST1 RNAi or control U6 plasmid maintained in membrane-depolarizing medium (30 mm KCl) or deprived of membrane depolarization (5 mm KCl) were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Representative images are shown (left, GFP-FOXO1; center, Hoechst; right, merged). Scale bar, 10 μm. Arrowheads indicate neurons displaying nuclear localization of FOXO1. D, quantification of results shown in Fig. 3C. MST1 knockdown significantly decreased GFP-FOXO1 nuclear accumulation in activity-deprived neurons. For each experiment, at least 100 neurons were counted (n = 3; p < 0.0001, ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD post hoc test).