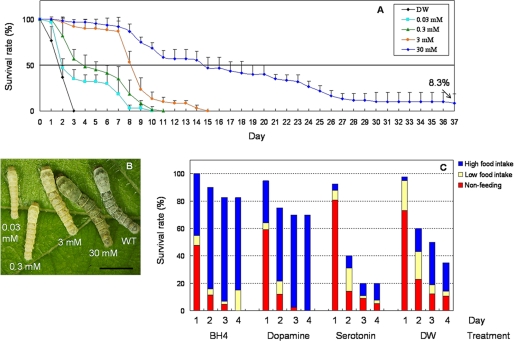
FIGURE 6.
Rescue of the leml lethal larvae by BH4 and monoamine administration. A, survival rate curves by different doses of BH4. Eggs of a65 strain were randomly divided into five parts. Mulberry leaves wetted by various concentrations of BH4 were fed daily to newly hatched larvae. From the beginning of the second instar (day 0), 40 leml/leml larvae were grouped and used in each treatment. Survival rate curves were plotted daily throughout the larval stage. Distilled water (DW) was used as a negative control. The points indicate the mean ± S.D. (n = 3). B, the phenotypes of the leml larvae in each BH4 treatment on day 2 of the third instar. WT, wild type. Scale bar, 1 cm. C, survival rates and feeding abilities of leml larvae with oral administration of dopamine and serotonin. Final concentration of monoamines was 50 mm. Forty leml/leml larvae at the beginning of third instar survived by 30 mm BH4 from first instar were used in each group. Survival rate curves were recorded from day 1 to day 4. Feeding abilities of the living larvae were examined by counting their feces: more than 10 feces, high food intake; 1-10 feces, low food intake; no feces, nonfeeding. BH4 (30 mm) and distilled water were used as control reagents.