Figure 1.
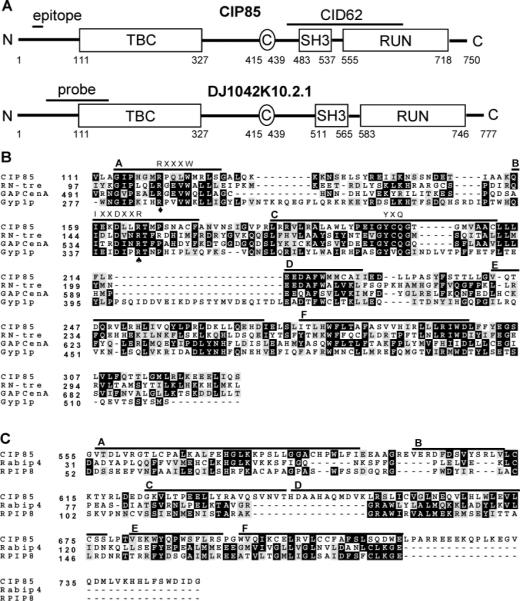
Homologues of CIP85 and their functional domains. Panel A, schematic diagram of CIP85 and a human CIP85 homologue (DJ1042K10.2.1). Both proteins contain TBC, SH3, and RUN domains and coiled coil (C) regions. The region corresponding to CID62 is shown, which encompasses the entire SH3 domain and the NH2-terminal half of the RUN domain of CIP85. The epitope region (Q31-KEESSEQPELCYDE45) used for preparation of the CIP85 antibody is shown. The cDNA probe used to detect the expression of CIP85 mRNA in human tissues by Northern blot analysis is also indicated. Panel B, multiple protein sequence alignment (Clustal W) of TBC domains from CIP85 of mouse (GenBank accession number AY382616), RN-tre of human (GenBank protein accession number NP_055503), GAPCenA of human (GenBank protein accession number NP_036329), and Gyp1p of S. cerevisiae (GenBank protein accession number Q08484). The black shaded areas represent residues matching the consensus sequence, and the gray shaded areas represent residues of conservative substitution. Three conserved “fingerprint” motifs (RXXXW, IXXDXXR, and YXQ) among the members of the Gyp protein family (42), in six shared regions named A–F, are shown (28). A spade denotes R165 in CIP85 that is conserved, and the corresponding site is critical for Gyp1p and Gyp7p GAP activity (26). A diamond denotes R120 in CIP85 that is conserved, and the corresponding site may play a role in the stabilization of the Gyp1p GAP domain (42). Panel C, multiple protein sequence alignment (Clustal W) of RUN domains from CIP85, Rabip4 (GenBank protein accession number NP_058039), and RPIP8 (GenBank protein accession number NP_058039) of mouse. Six shared regions named A–F are shown (31).
