Figure 5.
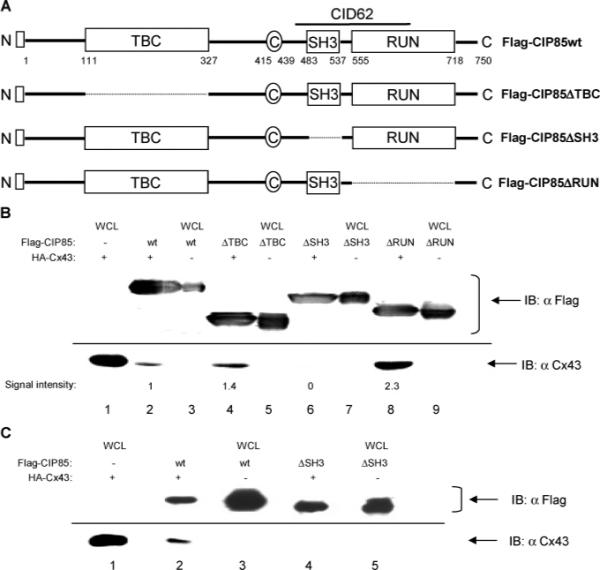
Identification of the Cx43-interacting domain in CIP85 by analyses of in-frame deletion mutants. Panel A, schematic diagrams of the CIP85 mutants with in-frame deletions of the TBC domain (ΔTBC), SH3 domain (ΔSH3), or RUN domain (ΔRUN). □: Flag epitope located at the NH2-terminus. Panel B, bacterial lysates containing Flag-CIP85wt (lane 2), the Flag-CIP85ΔTBC (lane 4), Flag-CIP85ΔSH3 (lane 6), or Flag-CIP85ΔRUN (lane 8) mutants were used in the in vitro interaction assays against HA-Cx43. The Flag-CIP85 present in the assays and the associated Cx43 were detected by immunoblotting with Flag or Cx43 antibodies (lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8). Bacterial lysates containing HA-Cx43 (lane 1), Flag-CIP85wt (lane 3), and the various mutants (lanes 5, 7, and 9) were used as positive controls to show the migration positions of these proteins. The signal intensities quantitated by densitometry were normalized for comparison. Panel C, affinity gel-purified Flag-CIP85wt (lane 2) and the Flag-CIP85ΔSH3 mutant (lane 4) were used in the in vitro interaction assays against HA-Cx43. The Flag-CIP85 present in the assays and the associated Cx43 were detected by immunoblotting with Flag or Cx43 antibodies (lanes 2 and 4). Bacterial lysates containing HA-Cx43 (lane 1), Flag-CIP85wt (lane 3), and Flag-CIP85ΔSH3 (lane 5) were used as positive controls.
