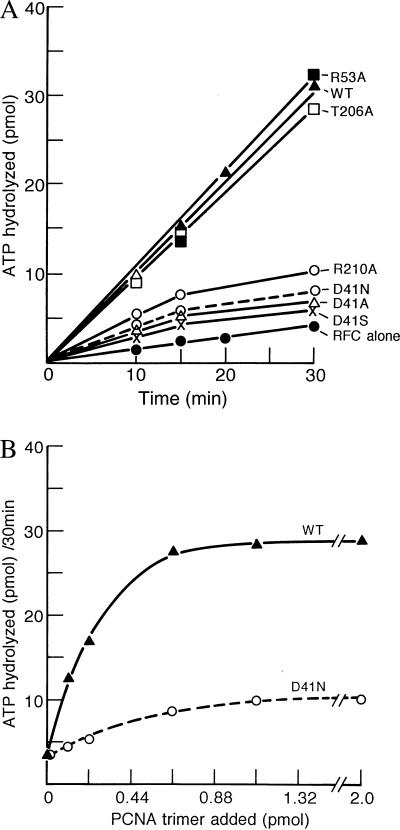
Figure 5.
Examination of the effects of various PCNAs on the DNA-dependent ATPase activity of RFC. (A) Influence of PCNA concentration on the DNA-dependent ATPase activity of RFC. Reaction mixtures (15 μl) contained 40 mM Tris⋅HCl buffer (pH 7.5), 1 mM DTT, 100 μg/ml BSA, 7 mM magnesium acetate, 0.33 mM [γ32P]ATP (10,000 cpm/pmol), 12.5 μM (as nucleotides) of poly(dA)300:oligo(dT)30 (1:5), 0.29 μg of hSSB, 1.5 pmol of indicated PCNAs, and 50 fmol of RFC. After incubation for 30 min at 37°C, 1-μl aliquots were spotted on polyethyleneimine-cellulose thin layer plates, which were developed in 1.0 M formic acid and 0.5 M LiCl for 20–30 min at room temperature. Plates were dried, were exposed for autoradiography, and were quantitated by excision and counting or by phosphorimager (Fuji) analysis. (B) Rate of ATP hydrolysis in the presence of various PCNA preparations. Reactions were carried out as described in A in the presence of 1.5 pmol of trimeric PCNAs. After 30 min of incubation, 1-μl aliquots were removed for analysis, as described in A.