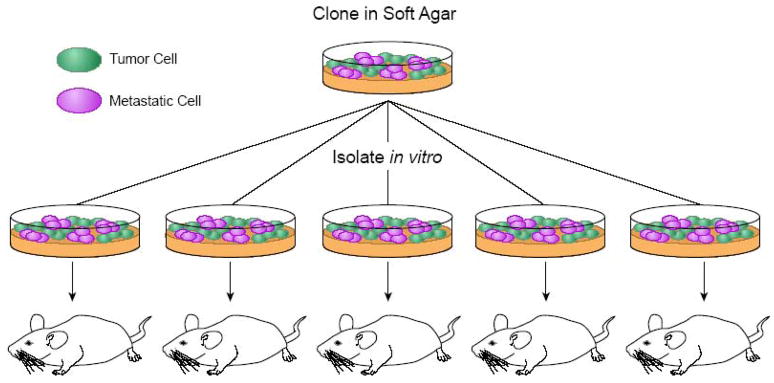
Figure 2. The Fidler Method of Metastatic Clone Isolation.
Adapted from Fidler [42,43]. Tumor cells from a non-isogenic B16 melanoma line are grown in soft agar and clones are picked for mouse injections. After 18 days, lung metastases are isolated and the procedure is repeated to enrich for a highly metastatic cell population. This method was used to determine whether the heterogeneity of the primary tumor cell line was due to the preexisting metastatic cells or whether the cells re-established metastatic cells based on the tumor microenvironment. These studies showed that metastasis was a coordinated and selective event rather than a random stochastic event.