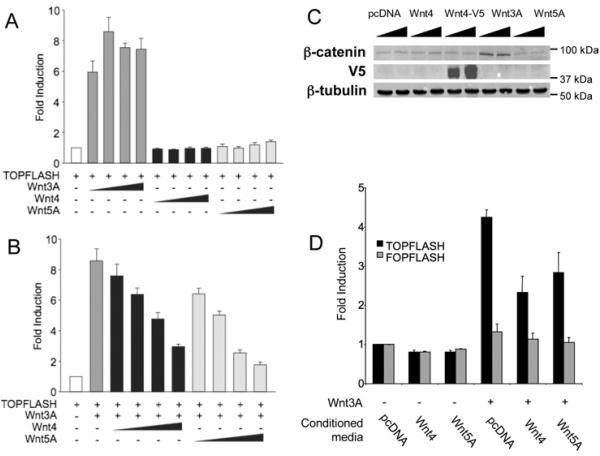
Figure 1. Wnt4 inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway.
(A) Wnt4 and Wnt5A do not activate the canonical Wnt pathway. Cells were co-transfected with TOPFLASH reporter plasmid (200 ng) and an increasing concentration of Wnt4, Wnt3A or Wnt5A expression plasmid (10, 40, 160 and 640 ng). (B) Wnt4 and Wnt5A inhibit Wnt3A-mediated signalling. Cells were co-transfected with TOPFLASH reporter plasmid (200 ng), Wnt3A expression plasmid (40 ng) to activate the canonical Wnt pathway and an increasing concentration of Wnt4 or Wnt5A expression plasmid (10, 40, 160 and 640 ng). (C) Wnt3A, but not Wnt4 and Wnt5A, affects β-catenin levels in cytoplasmic cell extracts. Cells were co-transfected with 500 ng and 1 μg of pcDNA or expression plasmids for Wnt4, Wnt3A and Wnt5 and β-catenin levels were assayed in Western blot on 10 μg of extract. Wnt4 expression was monitored by using V5-tagged Wnt4 plasmid (Wnt4–V5). Expression of β-tubulin was used as a loading control. (D) Media conditioned with Wnt4 and Wnt5A protein inhibit Wnt3A signalling. Cells were co-transfected with TOPFLASH reporter plasmid (100 ng) and Wnt3A (160 ng) and treated with conditioned media prepared from cells transfected with 1 μg of either pcDNA, Wnt4 or Wnt5A. Activities are expressed as fold activation of TOPFLASH activity in the presence of Wnt expression plasmid over that of empty vector. Results of each experiment are presented as the means±S.E.M. for three independent transfections.