Figure 3. Wnt4 redirects β-catenin to the cell membrane in vitro and in vivo.
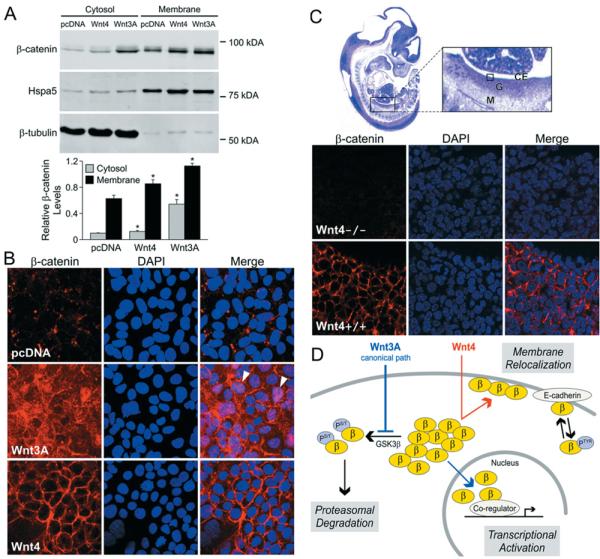
(A) Wnt4 increases β-catenin levels at the cytoplasmic membrane. Immunoblotting of β-catenin in subcellular fractions prepared from stably transfected cell lines. Hspa5, marker of membrane fraction, and β-tubulin, marker of cytosolic fraction, were used as purity and loading controls. Densitometric analysis is shown below and corresponds to three independent experiments. Relative β-catenin levels correspond to the ratio between β-catenin protein levels and the protein level for the matching fraction (Hspa5 for the membrane fraction or β-tubulin for the cytosolic fraction). Error bars represent the S.E.M. values. Two-tailed t test of paired sample means was performed between the control cell line (pcDNA) and Wnt-expressing cell line (Wnt4 or Wnt3A). *P < 0.05. (B) Immunofluorescence assay of β-catenin localization in cells stably transfected with empty vector pcDNA, Wnt3A or Wnt4. Arrowheads indicate nuclear staining; DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole), nuclear stain. (C) Immunofluorescence detection shows differential localization of β-catenin in Wnt4−/− compared with wild-type (Wnt4+/+) 12.5 dpc mouse ovaries. The boxed area within the enlarged image of the haematoxylin/eosin-stained full embryo section indicates the region depicted in the lower panels. Abbreviations: CE, coelomic epithelium of gonad; G, gonad; M, mesonephros. (D) Model depicting proposed mechanism of non-canonical Wnt4 action compared with the known mechanism of Wnt3A. Abbreviations: β, β-catenin; PS/T, serine/threonine phosphorylation; PTyr, tyrosine phosphorylation.
