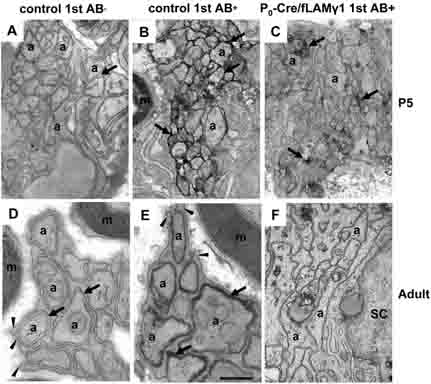
Figure 3. Homophilic and heterophilic interaction of N-CAM was impaired in mutant nerves.
At early developmental stages, immuno-EM shows that N-CAM is located at the site of apposed axons in control nerves (B) but is decreased in mutant nerves (C). When the non-myelinating SC/unmyelinated axon unit becomes mature and forms Remak bundles in the control nerves, N-CAM expression is restricted to the site between SC processes and axons (E), indicating that a homophilic or heterophilic interaction of N-CAM forms when axolemma adhere to the SC membrane. However, neither Remak bundles nor N-CAM staining are observed in the mutant nerves (F). Negative controls (no primary antibody) did not show staining in growing nerves (A) or in the Remak bundle of mature nerves (D). m, myelin sheath; a, axons; arrows, spaces between SC processes and axons or N-CAM-positive staining; arrowheads, SC processes. Bar: 4 mm (A-C); 3 mm (D-F).