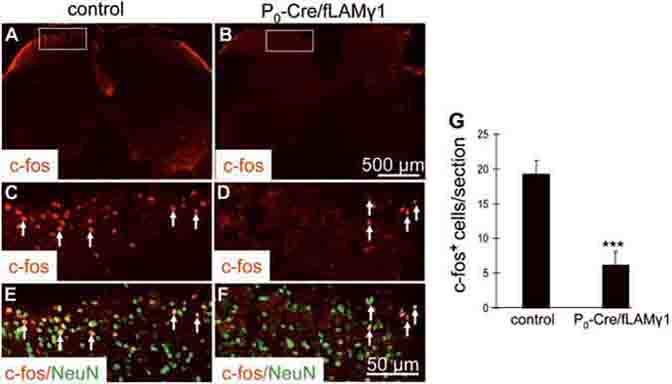
Figure 6. Heat stimulus-induced c-Fos expression in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord is impaired in mutant mice.
Immunostaining with anti-c-Fos antibody after immersion of the hind paw in a 52 °C water bath shows significantly fewer c-Fos-positive cells in the ipsilateral dorsal horn of lumbar 4/5 regions of the spinal cords of mutant mice (B, D, and F) than in those of control mice (A, C, and E). High magnification of boxed areas in A and B are shown in C and D, respectively. Merged images of double immunostainings for c-Fos and NeuN in boxed areas of A and B are shown in E and F, respectively. c-Fos-positive nuclei colocalized with NeuN immunostaining (E and F). Arrows: c-Fos- positive cells. (G) Quantitative analysis of c-Fos positive cells in sections of lumbar 4/5 spinal cord of control and mutant mice (4 representative serial sections from each animal; n=4 mice per genotype).