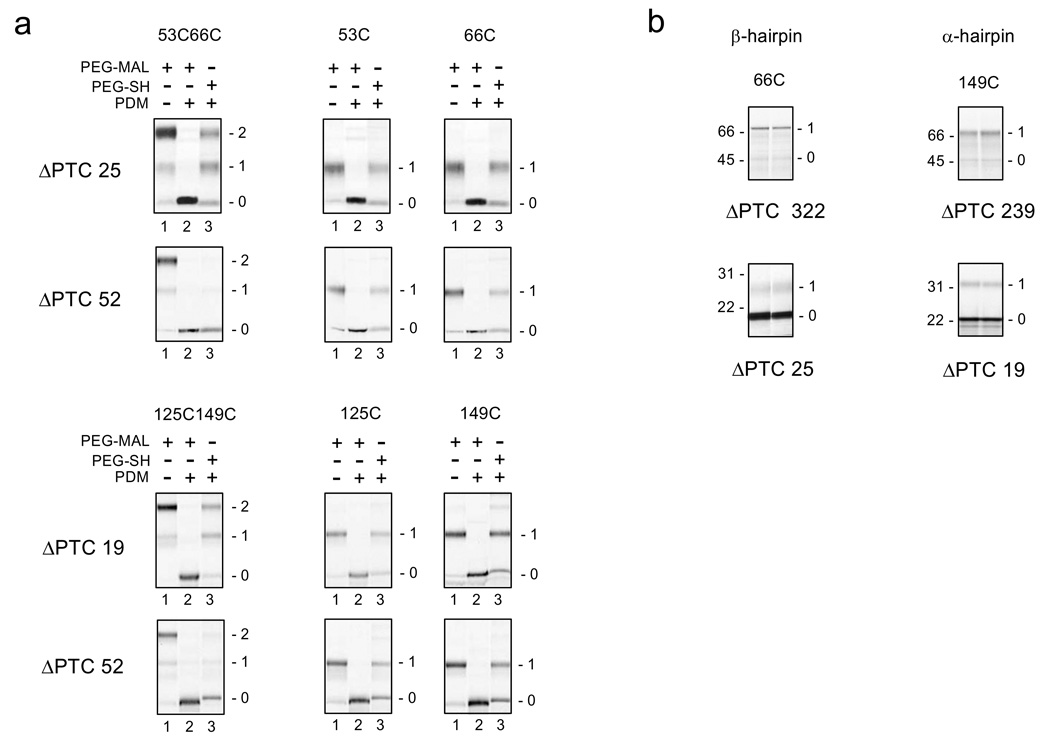
Figure 2. Crosslinking and Accessibility Assays for β- and α- Hairpins.
(a). Intramolecular crosslinking assay for indicated cysteine pairs (left column of gels) and single cysteines (two right-most columns of gels) for β-hairpin (top two rows) and α-hairpin (bottom two rows). The number of amino acids from the PTC to the C-terminal cysteine of the pair, or to the single cysteine, is indicated to the left of each row of gels as the ΔPTC. Engineered restriction sites, Xba I@91 and Kpn I@118, were used to produce ΔPTCs of 25 and 52, respectively, for the β-hairpin constructs. An engineered restriction site, BstE II@168, and a native site, Xba I@201, were used to produce ΔPTCs of 19 and 52, respectively, for the α-hairpin constructs. Numbers to the right of each gel represent doubly (2) or singly (1) pegylated or unpegylated (0) protein. In all cases, lane 2 background is significantly less than other lanes due to >95% labeling of the peptide with PDM, which leads to unpegylated protein that accumulates entirely in band 0. (b) Accessibility assays for C-terminal cysteines. Nascent peptides were pegylated as described in the Methods for 4 and 6 hours (lanes 1 and 2, respectively) for 66C (left column of gels) or 149C (right column of gels) in constructs with the indicated number of amino acids from the PTC to the C-terminal cysteine (ΔPTC). Long peptides (ΔPTC = 322 and 239), residing outside tunnel are shown in the top row of gels; short peptides (ΔPTC = 25 and 19) residing within the tunnel are shown in the bottom row of gels. Numbers to the left of each gel are molecular weight standards; numbers to the right of each gel represent singly (1) pegylated or unpegylated (0) protein.