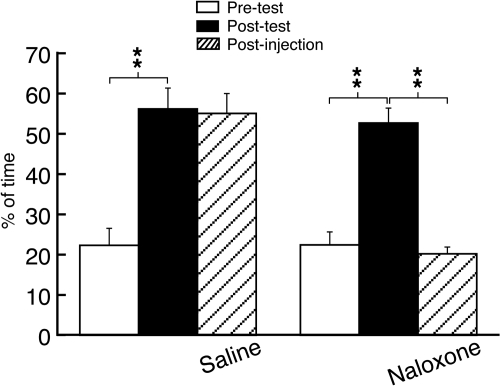
Fig. 1.
Conditioning treatment with repeated morphine induces the reward behavior of CPP through opioid receptors. Data were expressed as percentage of time the rat spent in the morphine-paired chamber versus the sum of the times spent in both morphine- and saline-paired chambers. Data of pretest (before morphine conditioning) and post-test (after morphine conditioning) were compared to determine the CPP behavior. One day after the post-test, a postinjection test was performed after an intraperitoneal injection of saline (n = 7 rats) or naloxone (1.5 mg/kg, n = 8 rats). **, p < 0.01.