Fig. 2.
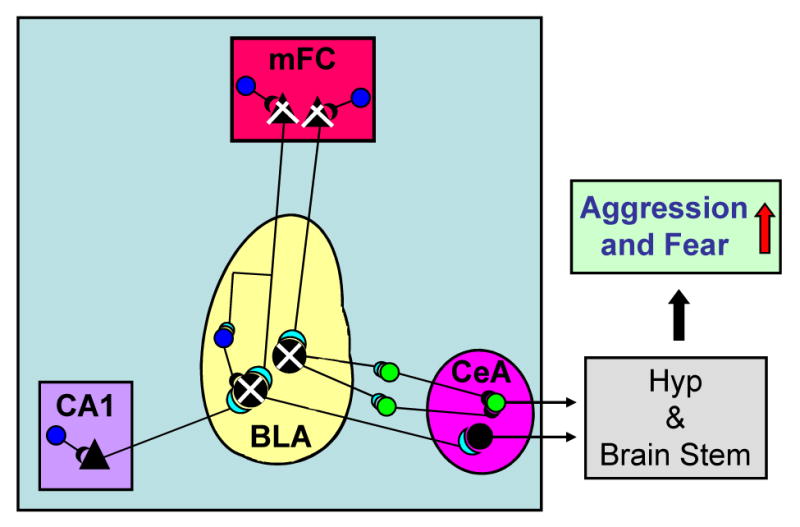
Schematic representation of the main intrinsic connections of the basolateral (BLA) and central (CeA) nuclei of the amygdala and extrinsic projections from the medial frontal cortex (mFC) (layer V/VI) and hippocampus (CA1) pyramidal neurons to the BLA.
In socially isolated mice, the decrease in Allo biosynthesis in layer V/VI pyramidal glutamatergic neurons of the mFC and in pyramidal-like glutamatergic neurons of the BLA (indicated by 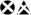 ) downregulates the inhibitory potency of GABAergic interneurons (indicated by
) downregulates the inhibitory potency of GABAergic interneurons (indicated by  ) impinging on these pyramidal neurons. This Allo content decrease results in an increased excitatory output from BLA to the intercalated (ITC) neurons or to neurons of the CeA nucleus, which project to the hypothalamus (Hyp) and brain stem, enhancing fear and aggression (indicated by
) impinging on these pyramidal neurons. This Allo content decrease results in an increased excitatory output from BLA to the intercalated (ITC) neurons or to neurons of the CeA nucleus, which project to the hypothalamus (Hyp) and brain stem, enhancing fear and aggression (indicated by  ).
).
 Pyramidal-like glutamatergic neurons expressing Allo
Pyramidal-like glutamatergic neurons expressing Allo
 Pyramidal glutamatergic neurons expressing Allo
Pyramidal glutamatergic neurons expressing Allo
 Inhibitory GABAergic interneurons
Inhibitory GABAergic interneurons
 Intercalated (ITC) GABAergic neuron
Intercalated (ITC) GABAergic neuron
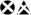 Decreased Allo biosynthesis in mFC pyramidal and BLA pyramidal-like glutamatergic neurons
Decreased Allo biosynthesis in mFC pyramidal and BLA pyramidal-like glutamatergic neurons
Modified from Sah and Westbrook [45].
