Fig. 5.
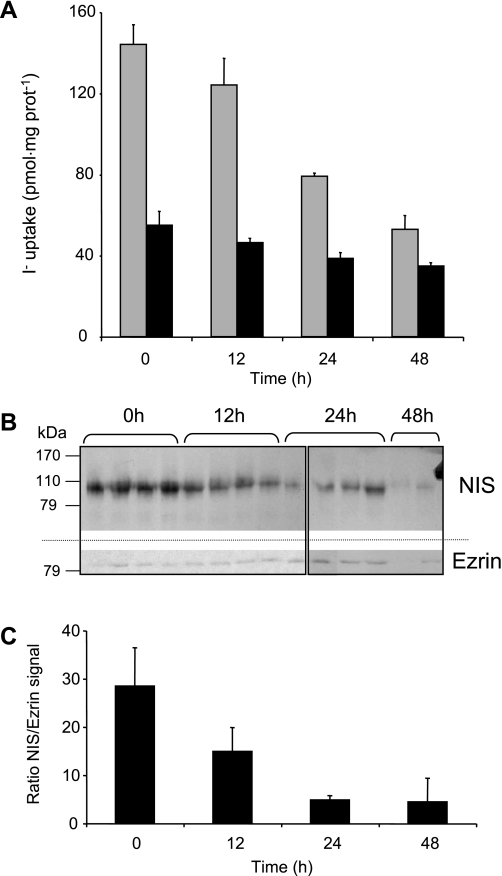
A high-I− diet reduces intestinal I− transport and NIS protein in vivo. Rats were provided water (control) or 0.05% KI-supplemented water. After the indicated times, BBMV were purified as described in materials and methods, and a steady-state I− uptake assay was performed (A) with 50 μg protein and 20 μM 125I− alone (gray bars) or in the presence of 80 μM ClO4− (dark bars). B: BBMV (100 μg) were also used for immunoblot and probed with anti-NIS and, after stripping the nitrocellulose, anti-ezrin antibodies. Ezrin was probed as a loading control, as described in materials and methods. Boxes indicate different gels. C: quantitation of the NIS/ezrin densitometric signal was done with ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD).