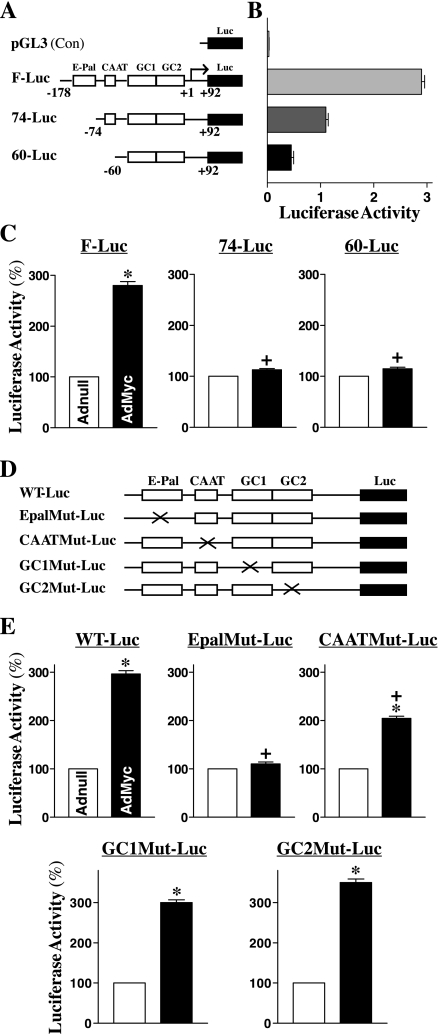
Fig. 3.
Effect of ectopic expression of the c-myc gene on E-cadherin promoter activity after mutation of different binding sites. A: schematic representation of deletion of E-cadherin promoter luciferase (Luc) reporter constructs. E-Pal, CAAT, GC1, and GC2 indicate the relative locations of specific binding sites within the E-cadherin-promoter. B: basal activity of various deletion mutants of the E-cadherin promoter in IEC-6 cells without c-Myc overexpression. Cells were transfected with different deletion mutants of E-cadherin-promoter, and levels of the luciferase reporter activity were detected 48 h after the transfection. Results were normalized relative to β-galactosidase activity from cotransfected plasmid pRSV β-galactosidase. Values are means ± SE of data from 3 separate experiments. C: changes in luciferase reporter activity of deletion constructs after c-Myc overexpression. Cells were infected with either the AdMyc or Adnull at s concentration of 10 pfu/cell for 24 h and then transfected using different E-cadherin promoter luciferase reporter deletion constructs. The levels of luciferase activity was assayed 48 h after transfection. Values are means ± SE of data from 3 separate experiments. *P < 0.05 compared with cells transfected with the Adnull. +P < 0.05 compared with cells infected with the AdMyc and then transfected with the F-Luc. D: schematic representation of various point mutants. Mutagenic oligonucleotides were designed to hybridize to the E-cadherin-promoter construct to create the mutant (Mut) where the E-Pal, CAAT, GC1, or GC2 consensus site was eliminated by making 2 base changes. E: levels of reporter gene activity. Values are means ± SE of data from 3 separate experiments. *P < 0.05 compared with cells infected with the Adnull. +P < 0.05 compared with cells infected with the AdMyc and then transfected with the WT-Luc.