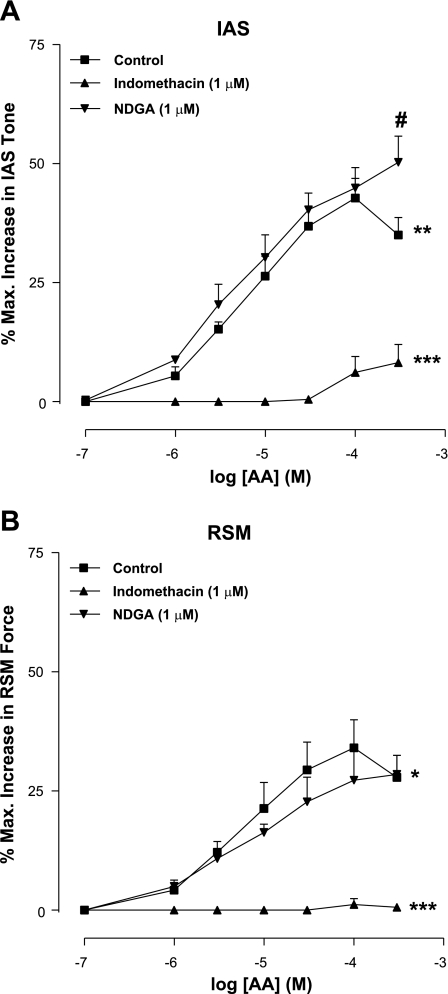
Fig. 1.
Cumulative concentration-response curves for arachidonic acid (AA), showing significant increase in the internal anal sphincter (IAS) tone (A) and rectal smooth muscle (RSM) force (B; *P < 0.05). AA is more efficacious and potent in producing increase in the IAS tone versus force in the RSM (**P < 0.05). Indomethacin causes significant attenuation of AA effects both in the IAS and RSM (***P < 0.05). #P < 0.05. Data represent means ± SE of 4 independent determinations. NDGA, nordihydroguaiaretic acid.