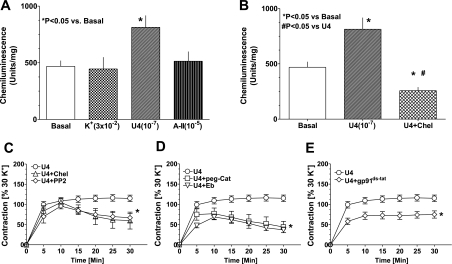
Fig. 6.
A PKC and Src kinase stimulation of Nox oxidase generated increases in superoxide generation, and elevated hydrogen peroxide contributes to the contraction of coronary arteries by U46619. A: effect of 30 mM KCl (K+), 100 nM U46619 (U4), and 10 μM angiotensin II (A-II) on coronary arterial superoxide detected by 5 μM lucigenin. U46619 significantly elevated superoxide levels. B: treatment of coronary artery with chelerythrine (10 μM) for 30 min before the application of U46619 decreased superoxide generation. C: chelerythrine (10 μM) and PP2 (10 μM) partially blocked the sustained, but not the initial, contraction to U46619. D and E: hydrogen peroxide scavengers ebselen (Eb; 10 μM) and peg-catalase (peg-cat; 150 U/ml) (D) and the NADPH oxidase inhibitor gp91ds-tat (50 μM) (E) decreased both the initial and sustained contraction to PDBu. C and E: P < 0.05 vs. U4.