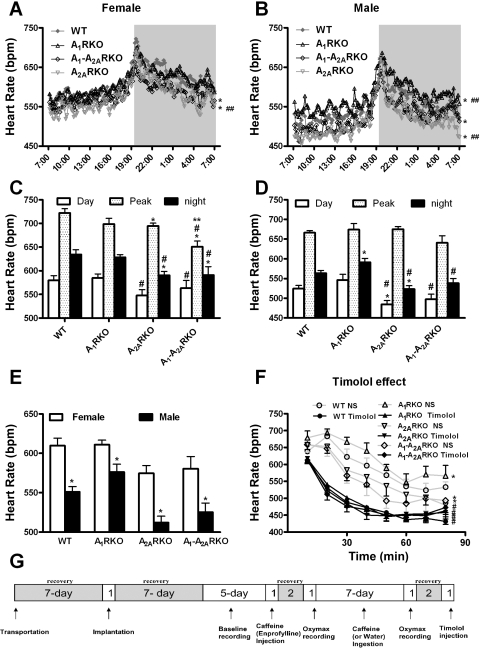
Fig. 1.
A1 and A2A adenosine receptors (A1R or A2AR, respectively) affect heart rate (HR) in sex-dependent manner. A and B: HR is recorded for consecutive 10-min periods in wild-type [WT; Female (F), n = 8; Male (M), n = 8], A1R-knockout (A1RKO; F, n = 8; M, n = 8), A2ARKO (F, n = 8; M, n = 10), and A1-A2ARKO (F, n = 8; M, n = 9) mice. The dark period is from 7 PM to 7 AM. C and D: summarizing the corresponding top panels. The value for Day shows the HR average between 9 AM and 5 PM; the value for Night shows the HR average between 9 PM and 5 AM; the value for Peak shows the HR average between 7:30 PM and 7:40 PM. In A–D, data are shown as a 5-day average; data are presented as mean values or mean values ± SE (*P < 0.05 compared with WT mice; #P < 0.05 compared with A1RKO mice; **P < 0.05 compared with A2ARKO mice; ##P < 0.05 compared with A1-A2ARKO mice at the corresponding time period). E: HR was measured telemetrically during 24 h. The data are shown as a 5-day average and presented as mean values or mean values ± SE (*P < 0.05 compared with corresponding female mice). F: effects of saline and timolol (1 mg/kg) on HR in male mice. The HR was measured at 10-min intervals until 80 min after injection. Data are presented as means ± SE (*compared with WT, P < 0.05; #compared with saline injection, P < 0.05). Abbreviations and mice number are the same as above. G shows the protocol of experiments. bpm, Beats/min; NS, saline.