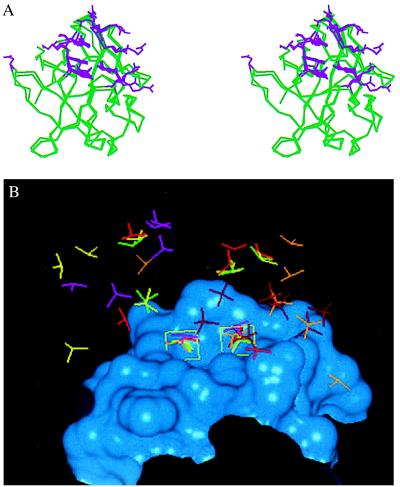
Figure 5.
(A) Stereo diagram comparing the residues involved in saccharide binding for FGF-1 and FGF-2. The Cα trace of the following FGF cocrystal structures are superimposed: 1AFC, 1AXM, 1BFB, 1BFC, 1BAS, and the cocrystal of FGF-2 with disaccharides and trisaccharides. For sake of clarity the Cα trace of one FGF-2 molecule and one FGF-1 molecule are shown (green). The side-chain atom positions of the amino acid residues that interact with the HLGAG fragments in each of the structures are shown (violet). Note that more than eight of the side-chain conformations at the center of the heparin-binding region are almost identical and are found to interact with the HLGAG in all of the cocrystal structures (FGF-1 and FGF-2). Residues K27 and N102 of FGF-2 (on the left with only one side chain shown) are observed to interact only in the FGF-2 hexasaccharide cocrystal and have been identified as the secondary heparin binding site (21). Residues R116 and R119 of FGF-1 (on the right with side chain from only one structure shown) represent the additional FGF-1 residues identified to interact with SOS. Notably, the side chains of both FGF-1 and FGF-2 that interact with the cognate HLGAG fragments are topologically very similar. (B) Position of sulfates in bound to FGF-1 or FGF-2 in the cocrystal structures. The heparin-binding region of FGF-2 is represented as a Connolly surface (blue). Only the sulfate groups of the ligands are compared, and the HLGAG sugar atoms are not shown. The following ligands are shown: SOS (dark red), hexasaccharide (yellow), tetrasaccharide (green), decasaccharide 1 (light red, see below), decasaccharide 2 (orange, see below), and decasaccharide 3 (pink, see below). DiGabriele et al. (15) report three different modes of HLGAG decasaccharide binding to FGF-1, one in which the decasaccharide is bound with reversed polarity (decasaccharide 2) compared with the other (decasaccharide 1) and a third where the decasaccaharide is shifted by about two saccharide units (decasaccaharide 3). Notice that the position of two of the sulfates in all of these structures are identical (shown inside green boxes). For the box on the left, all of the sulfates (except SOS and decasaccaharides 2 and 3) are linked to the 2-O of the iduronate, whereas the decasaccaharide 2 sulfate belongs to the N position of the glucosamine and the decasaccaharide 3 sulfate belongs to the 6-O position of the glucosamine. Similarly for the box on the right, all of the sulfates except SOS, decasaccaharide 2, and decasaccaharide 3 belong to the N sulfate of the glucosamine whereas the decasaccaharide 2 and decasaccaharide 3 sulfates are from the 2-O position of the iduronate.