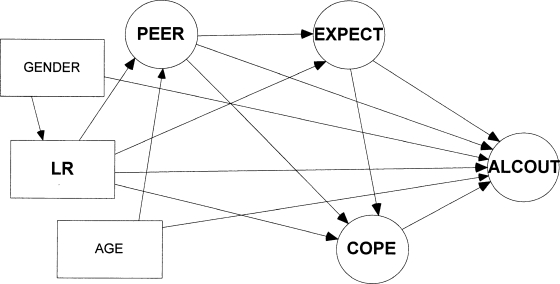
Figure 1.
The hypothesized level of response (LR)-based model with a low LR to alcohol hypothesized to relate directly to alcohol-related outcomes (ALCOUT) as well as through heavier drinking in peers (PEER), higher positive expectancies of the effect of alcohol (EXPECT), and learning to use alcohol to cope with stress (COPE). The relationships of PEER and EXPECT to ALCOUT are also hypothesized to be at least partially mediated by COPE. GENDER is hypothesized to be related to both LR and ALCOUT. AGE is hypothesized to be related to PEER and ALCOUT.