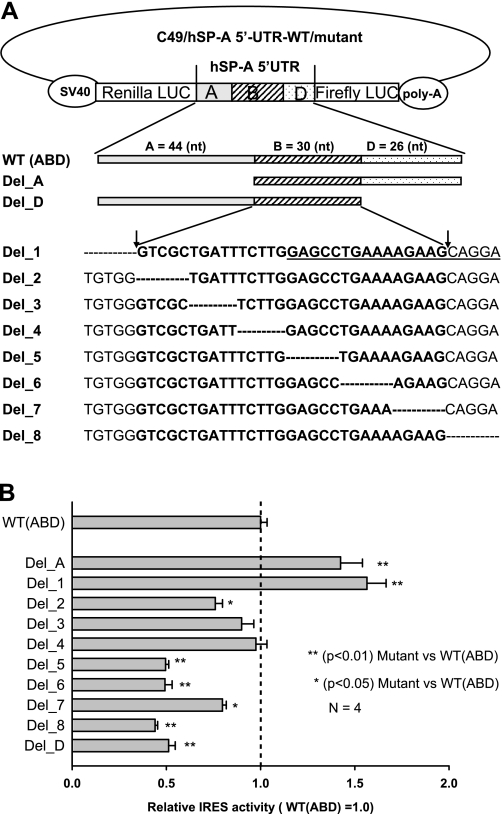
Fig. 5.
Analysis of cis-acting elements through a series of deletion mutations and IRES activity assay. A: diagram of deletion mutations of the bicistronic ABD construct. hSP-A 5′-UTR ABD fragment, consisting of exons A, B, D, is located between Renilla and firefly reporter genes. First, 2 exon deletion mutants (Del_A and Del_D) were produced through the deletion of the entire exon A or exon D, respectively. Second, 8 deletion mutants (Del_1 to Del_8) were generated, each of which has 5 bp removed within the exon B region or in its boundaries to exon A and D. The wild type (WT) (ABD) is listed above the mutants and used as positive control. An adenosine-rich short motif is underlined in the sequence of Del_1. B: changes of IRES activity in the deletion mutants, compared with the WT (ABD) construct. After transfection with mutants as well as the WT construct, the H441 cells were harvested at 36 h after transfection. Both Renilla and firefly luciferase activities were determined as described in materials and methods. Ratio of firefly to Renilla luciferase activities is used to represent the IRES activity of each mutant. To compare IRES activities of the mutants and the WT, relative IRES activity was calculated. The WT (ABD) IRES activity (ratio of firefly to Renilla luciferase) was set as 1.0, and the relative IRES activity of each mutant was equal to the value of the IRES activity of each mutant divided by the IRES activity of the WT. IRES activities of mutants Del_A and Del_1 were significantly higher (P < 0.01) than that of the WT; IRES activities of Del_D, Del_5, Del_6, and Del_8 were significantly lower (P < 0.01) than that of the WT; mutants Del_2 and Del_7 had lower (P < 0.05) IRES activities compared with the WT but higher IRES activities than most of the other mutants (Del_D, Del_5, Del_6, and Del_8). Experiments were repeated 4 times (n = 4). Bars show ±SE.