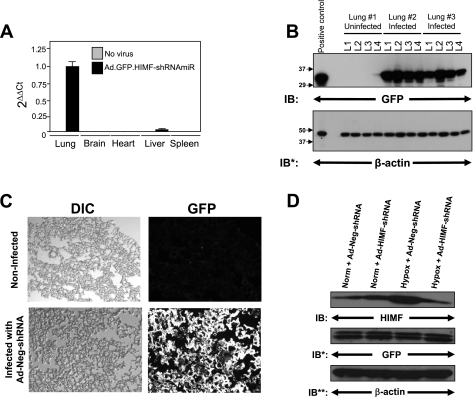
Fig. 1.
In vivo knockdown of hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor (HIMF) in the chronic hypoxia model of pulmonary hypertension. A: real-time PCR for green fluorescent protein (GFP) from RNA isolated from the lung, heart, liver, and spleen 72 h after intratracheal instillation of Ad-HIMF-shRNA. B: equally divided left lungs from uninfected rats or rats infected with Ad-Neg-shRNA 4 days earlier were homogenized and evaluated for GFP expression. The homogenates were resolved by 4–20% SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. The blots were probed with rabbit polyclonal anti-GFP antibodies and developed with ECL. To confirm equal protein loading and transfer, the blots were stripped and reprobed with monoclonal anti-β-actin antibodies. IB, immunoblot; IB*, immunoblot after stripping. C: visualization of GFP in control rat lungs or lungs infected with Ad-Neg-shRNA. DIC, differential interference contrast. D: lung homogenates from animals exposed to 4 days of normoxia (20.8% O2) or hypoxia (10.0% O2) were evaluated for HIMF expression. The homogenates were resolved by 4–20% SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. The blots were probed with polyclonal anti-HIMF antibodies and developed by ECL. To confirm introduction of the viral vectors, the blot was stripped and reprobed with polyclonal anti-GFP antibodies. To confirm equal protein loading, the blots were stripped and reprobed with monoclonal anti-β-actin antibodies. IB**, immunoblot after second stripping.