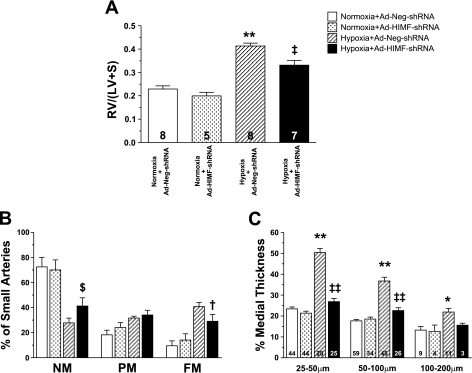
Fig. 2.
In vivo knockdown of HIMF reduces hypoxia-induced vascular remodeling. A: the histogram shows means ± SE of right ventricular weight/(left ventricular + septal weight) [RV/(LV+S)] of rats exposed to 14 days of normoxia (20.8% O2) or hypoxia (10.0% O2) following intratracheal instillation of Ad-Neg-shRNA or Ad-HIMF-shRNA. The number of animals studied is indicated within each bar. B: muscularization of small pulmonary arteries is indicated as non-muscular (NM), partially muscular (PM), or fully muscular (FM) in rat lungs from the 4 different groups of rats as stated. C: comparison of percent medial wall thickness of pulmonary arteries 25–50 μm, 50–100 μm, and 100–200 μm among the 4 groups of rats. The number of vessels counted is indicated within each bar. *Significantly increased vs. normoxia+Ad-Neg-shRNA control at P < 0.05. **Significantly increased vs. normoxia+Ad-Neg-shRNA control at P < 0.001. $Significantly increased vs. hypoxia+Ad-Neg-shRNA control at P < 0.05. †Significantly decreased compared with hypoxia+Ad-Neg-shRNA control at P < 0.05. ‡Significantly decreased compared with hypoxia+Ad-Neg-shRNA control at P < 0.01. ‡‡Significantly decreased compared with hypoxia+Ad-Neg-shRNA control at P < 0.001.