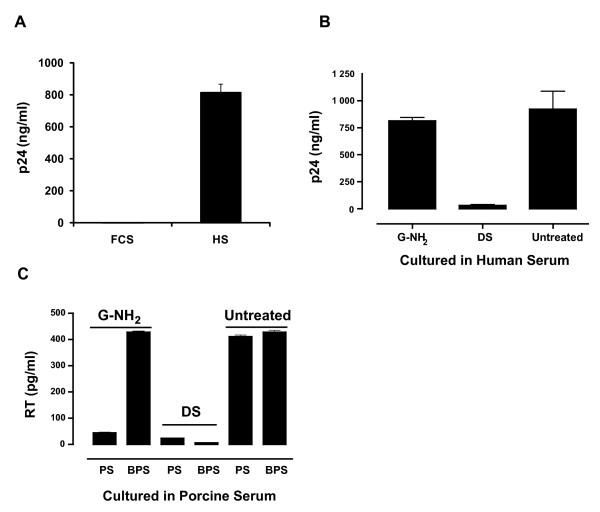
Figure 1.
Antiviral activity of G-NH2 and characterization of G-NH2 metabolite obtained after dialysis against FCS or PS. (A) H9 cells (105) were infected with the SF-2 strain of HIV-1 and cultured in medium containing 100 μM G-NH2 and either 10% fetal calf serum (FCS) or human serum (HS). Ten days post-infection, the level of p24-antigen in the culture supernatants was assayed with a p24-ELISA. (B) H9 cells infected with the SF-2 strain of HIV-1 were cultured in medium containing 10% human serum (HS) and either 100 μM G-NH2 or a dialysis solution (DS) of 1/10 dilution of 1 mM G-NH2 dialyzed against FCS. Untreated cultures without any addition of G-NH2 or DS served as controls. (C) Infected H9 cells were cultured in the presence of 10% boiled porcine serum (BPS) or non-boiled porcine serum (PS). The infected cultures were cultured with the addition of 100 μM G-NH2, DS or were left untreated. Virus production was assessed using an RT assay. Error bars indicate standard deviations from quadruple cultures.