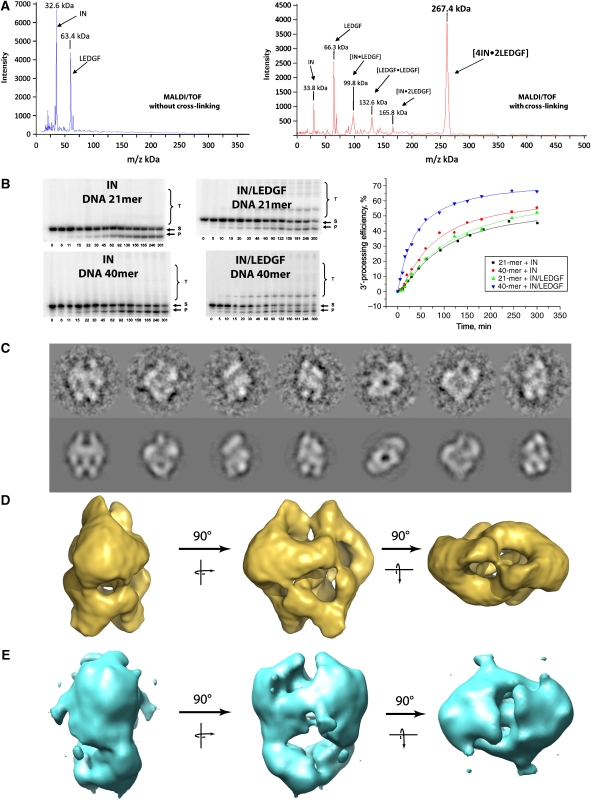
Figure 1.
Functional characterisation and structure determination of the IN/LEDGF complexes. (A) IN/LEDGF complex analysis by high-mass MALDI mass spectrometry in the absence and presence of cross-linking agent showing a major peak of (IN)4–(LEDGF)2. (B) Kinetic study of the 3′ processing and strand-transfer reactions catalysed by HIV-1 integrase or by the IN–LEDGF complex using a 21- or 40-mer DNA substrate. Bands correspond to substrate DNA (S), 3′-processed product (P) and strand-transfer product (T). Incubation times are in min. The bands intensities are reported as a function of time, showing the increase of the 3′ processing kinetic when using the IN–LEDGF complex with a 40-mer DNA substrate. (C) Views of the cryo negatively stained IN/LEDGF complex (upper row) and the corresponding reprojections of the 3-D model (lower row). (D) The 3-D model of the cryo negatively stained IN/LEDGF complex. (E) The 3-D model of the cryo negatively stained IN/LEDGF complex in the presence of the 21-bp DNA substrate.