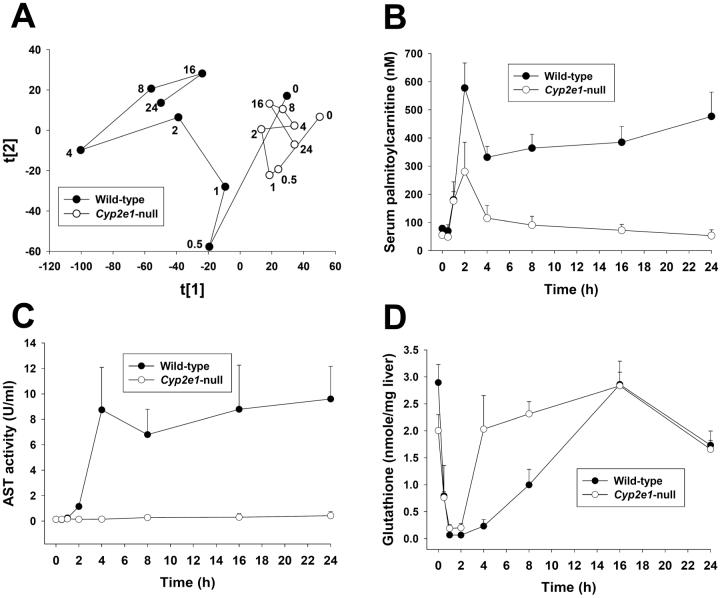
Figure 3.
Time-dependent changes in wild-type and Cyp2e1-null mice following 400 mg/kg APAP treatment and comparison of the biomarkers of APAP toxicity. Serum and liver samples were collected at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 24 h after APAP treatment. A, Scores plot of PCA analysis on serum metabolomes. Details of data acquisition, processing and model construction were described in the Experimental procedures. Each data point represents the average of 4-8 samples in each sample group (wild-type mice: • and Cyp2e1-null mice: ○). The timing of sample collection was labeled beside the data point. The t[1] and t[2] values represent the scores of each sample group in principal component 1 and 2, respectively (Supplemental Figure 2A). Fitness (R2) and prediction power (Q2) of this PCA model are 0.388 and 0.251, respectively. B, Quantitation of serum palmitoylcarnitine level in wild-type and Cyp2e1-null mice (mean ± SD, n=4 mice/group). Palmitoylcarnitine levels in serum was measured using the multiple reactions monitoring mode in LC-MS. [2H3]palmitoylcarnitine was used as internal standard. C, Time course of AST activity in wild-type and Cyp2e1-null mice (mean ± SD, n=4). D, Time course of hepatic glutathione level in wild-type and Cyp2e1-null mice (mean ± SD, n=4). Glutathione level in liver was measured using the multiple reactions monitoring mode in LC-MS.