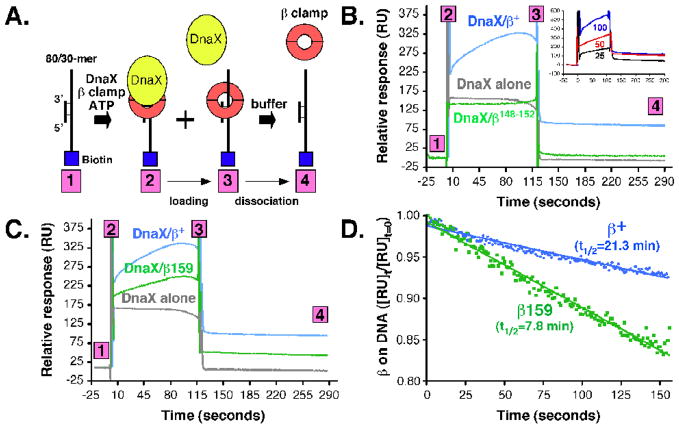
FIGURE 3. Ability of DnaX to load wild type or mutant clamps onto a linear primed DNA template.
(A) The approach used for measuring clamp loading and retention of the clamp on DNA is depicted in cartoon form. Clamp loading reactions contained 50 nM DnaX complex and 250 nM (as dimer) of β+ or β148–152 (B), or β+ and β159 (C) in HBS-EP buffer lacking EDTA and supplemented with 1 mM ATP and 10 mM MgCl2. The level of DnaX used was determined experimentally based on a titration of DnaX (25 [black], 50 [red], or 100 nM [blue]) using a fixed level of β+ (250 nM), as shown in the inset to panel (B). (D) The half-life for the stability of clamp on DNA was measured by plotting the change in RU signal as a function of time. Half-life was measured using results contained between step 3 and step 4 of the results shown in panels (B) and (C).