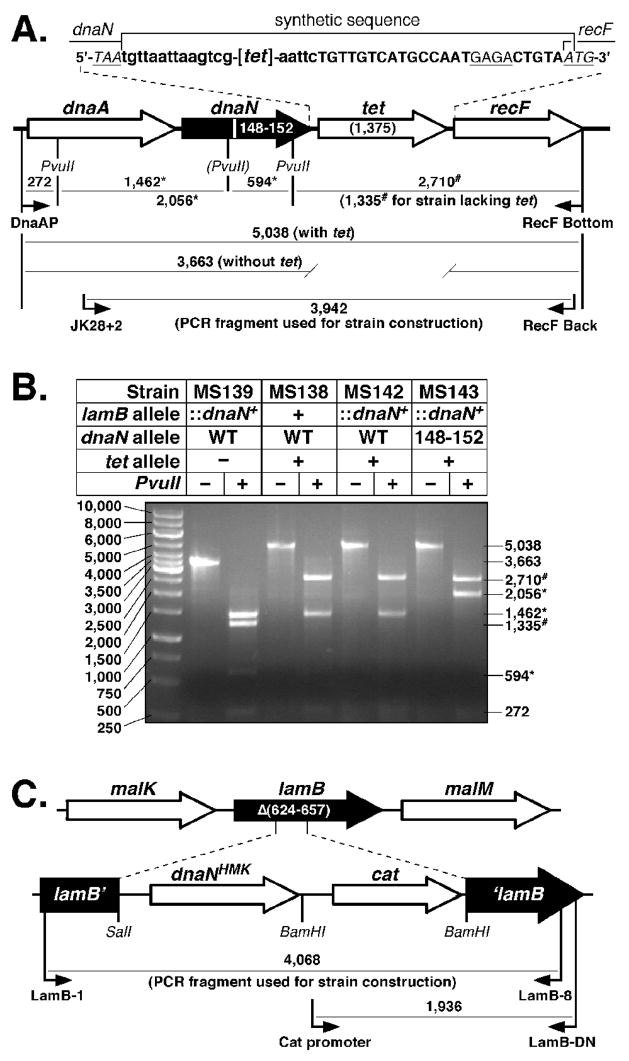
FIGURE 5. Construction of tagged dnaN+ and dnaN148–152 E. coli strains.
(A) Physical map of the dnaA operon depicting the structure of the dnaA-dnaN+-tet-recF and dnaA-dnaN148–152-tet-recF alleles. The specific DNA sequence flanking the tet gene is indicated. Nucleotide sequence depicted in lower case flanking the tet coding sequence ([tet]) was inserted as part of the tet cassette as described in Materials and Methods. The Shine Delgarno sequence for recF is underlined, and the stop (TAA) and start (ATG) codons for dnaN and recF, respectively, are indicated. The PvuII restriction site that is disrupted in the dnaN148–152 allele is indicated by parentheses. Predicted sizes of PvuII restriction fragments for the dnaA-dnaN+-tet-recF and dnaA-dnaN148–152-tet-recF alleles are indicated. (B) Representative results from PvuII restriction digestion of the PCR-amplified dnaA operon region from dnaN+ lamB::(His6-dnaN+-cat) (MS139), dnaA-dnaN+-tet-recF (MS138), dnaA-dnaN+-tet-recF lamB::(His6-dnaN+-cat) (MS142), and dnaA-dnaN148–152-tet-recF lamB::(His6-dnaN+-cat) (MS143) strains are shown. The asterisk (*) denotes those fragments resulting from the loss of the PvuII restriction site in dnaN148–152. The number sign (#) denotes those fragments resulting from insertion of the tet cassette between dnaN and recF. (C) Physical map of the lamB locus depicting the structure of the lamB::(His6-dnaN+-cat) cassette. Primers used for strain construction or for diagnostic PCR to confirm the structure of the insertion in strain MS139, as well as sizes for respective PCR products are shown.