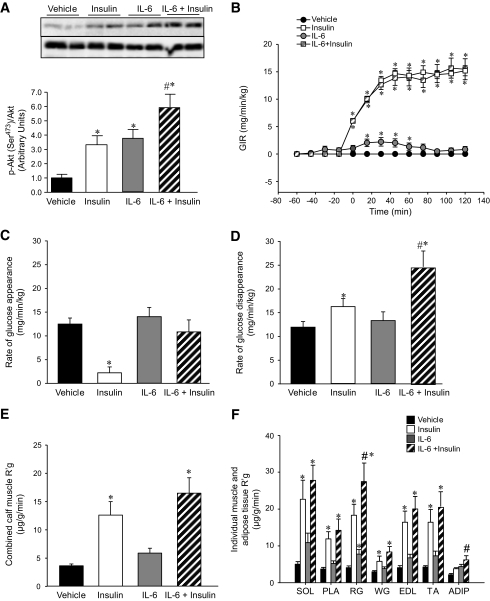
FIG. 6.
IL-6 augments insulin action in muscle and fat but results in hepatic insulin resistance in vivo. Representative blots and quantification of phosphorylation (Ser473 )/total Akt in mixed hindlimb muscle (A), GIR (B), rate of glucose appearance (C) and disappearance (D), combined calf muscle glucose uptake (R′g) (E) and individual hindlimb muscle (SOL, soleus; PLA, plantaris; RG, red gastrocnemius; WG, white gastrocnemius, EDL, extensor digitorum longus; TA, tibialis anterior) and adipose tissue (ADIP) (F) from rats that underwent control (vehicle) and euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamps (insulin 3 mU · min–1 · kg–1 ) for 120 min with and without the infusion of IL-6 (5.0 μg · h–1 · kg–1 ). *Difference (P < 0.05) from vehicle; #difference IL-6 + insulin versus insulin (data are means ± SE; n = 6).