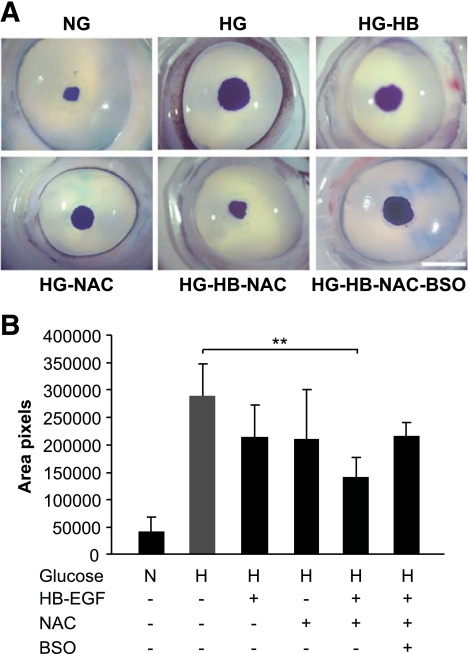
FIG. 7.
Effects of HB-EGF and NAC on corneal epithelial wound healing in high-glucose conditions. A: Representative epithelial wound closure in cultured porcine corneas. A corneal epithelial wound of 5-mm diameter was made and allowed to heal in MEM containing normal glucose (NG; 5 mmol/l d-glucose) and in high glucose (HG; 25 mmol/l d-glucose) alone or in the presence of HB-EGF (HG-HB; 50 ng/ml), with (HG-HB-NAC) or without NAC (HG-NAC; 25 μmol/l) and BSO (HG-HB-NAC-BSO; 250 μmol/l) for 48 h, followed by Richardson staining to show the remaining wound. B: Remaining wound area after 48 hours. Changes in the means of the remaining wound area in pixels were analyzed by ANOVA. Data are the means ± SD of at least six corneas from three independent experiments. **P < 0.01. Scale bar = 5 mm. H, high; N, normal. (A high-quality digital representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)