Fig. 10.
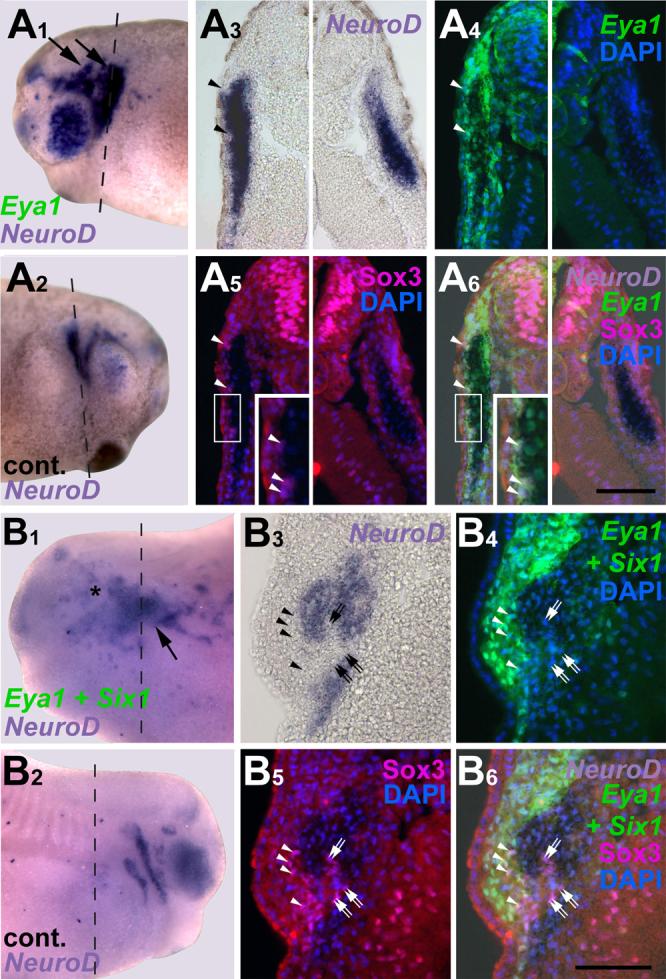
Ectopic neurons in embryos overexpressing Eya1 or Eya1+Six1 originate from Sox3 immunopositive neuronal progenitors. Panels show distribution of NeuroD expressing cells in relation to Sox3-immunopositive cells in tail bud stage embryos after injection of myc-Eya1 mRNA alone (A) or together with Six1 mRNA (B). Embryos are shown as wholemounts (injected side: A1-B1; control side: A2-B2) and in transverse sections (at level indicated by black line). Panels show bright field images (A3-B3), myc-immunostaining together with DAPI (A4-B4), Sox3-immunostaining together with DAPI (A5-B5), and merged images (A6-B6). Asterisks indicate reductions, while arrows mark ectopic NeuroD expression in the non-neural ectoderm. Ectopic NeuroD expression is found next to Sox3 immunopositive cells on the fringes of ectodermal regions that received high levels of myc-Eya1. Sox3 cells reside in ectoderm that received high levels of myc-Eya1 (arrowheads) as well as in areas of lower myc-Eya1 levels immediately abutting NeuroD expressing cells (double arrows). Boxed areas are shown at higher magnifiction in inserts. All bars: 100 μm
