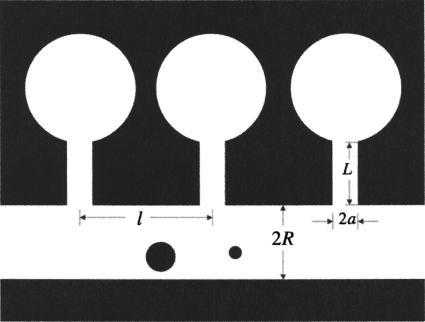
Figure 1.
A tube of radius R with identical periodic dead ends separated by distance l. Dead ends are formed by cavities of volume Vcav connected to the tube by narrow channels of radius a and length L. The larger particle cannot enter the dead ends since its size exceeds the size of the dead end entrance. The smaller particle is capable of entering the dead ends that work as reversible traps for this particle, which slow down its diffusive spreading along the tube axis.