Figure 2.
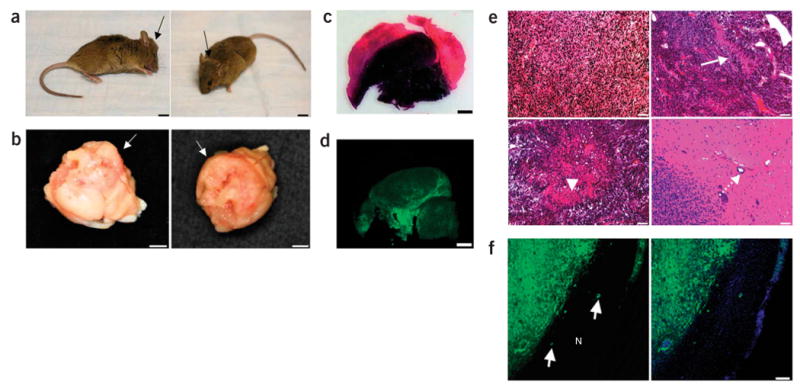
Brain tumors induced by combined activation of H-Ras and AKT in GFAP-Cre mice. (a) Representative images of GFAP-Cre mouse showing tumor formation. A GFAP-Cre mouse injected with Tomo H-RasV12 LVs into the right hippocampus showed an enlarged head (black arrows) 93 d after the injection. Scale bars, 5 mm. (b) Photograph showing gross appearance of the brain, suggesting a massive lesion in the cerebrum. White arrows indicate the irregular surface of the cerebrum. Scale bars, 3 mm. (c) Representative image of an H&E-stained section (40 μm). A darker area indicates increased cellular density of the tumor. Scale bars, 1.5 mm. (d) Representative confocal image of a section (40 μm). GFP+ cells are found throughout the tumor. Scale bars, 1.5 mm. (e) H&E staining showing the characteristics of glioma, including increased cell density (top left panel), pseudopalisading (top right panel, white arrow), necrosis within the dense cellular region (bottom left panel, arrowhead) and perivascular invasion (bottom right panel, dotted arrow). Scale bars, 50 μm. (f) Tumor section (40 μm) analyzed by confocal microscopy. White arrows in the left panel show invasion of the GFP+ tumor cells into normal tissues (indicated by N). A merged image with DAPI (blue) is shown in the right panel. Scale bar, 100 μm.
