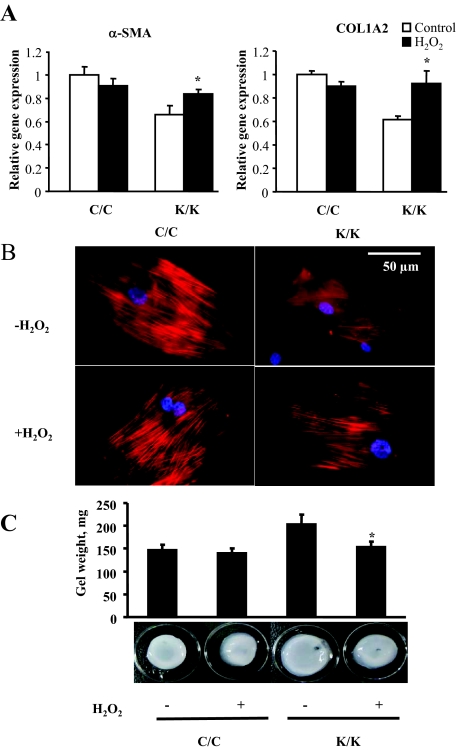
Figure 8.
H2O2 rescues the phenotype of Rac1-deficient fibroblasts. Fibroblasts were isolated by explant culture from mice containing the Rac1 gene (C/C) or not (K/K). A: Cells incubated in the presence or absence of 200 μmol/L H2O2 for 24 hours were fixed and stained with anti-α-SMA antibody to detect α-SMA. Rac1-deficient cells in the presence of H2O2 possessed α-SMA stress fibers indicating restored myofibroblast formation. Fibroblasts from four mice per group were used. Representative data are shown. B: Real-time PCR analysis. mRNA harvested from cells in the presence or absence of 200 μmol/L H2O2 for 24 hours (Fibroblasts from four mice per group were used, each assay was performed in triplicate, average ± SD is shown) and subjected to real-time PCR analysis to detect the mRNAs indicated. Data represent averages and SD from all these mice. (*P < 0.05, Student’s t-test). C: Addition of 200 μmol/L H2O2 to Rac1-deficient fibroblasts rescues the ability of fibroblasts to contract a collagen gel matrix: Floating gel analysis. The effect of loss of Rac1 expression on ECM contraction generated by fibroblasts embedded in a floating collagen gel matrix was assessed over a 24 hour period in the presence and absence of 200 μmol/L H2O2. Contraction was assessed photographically (N fibroblasts from three separate animals were used, and experiments were performed in triplicate; Average ± SD is indicated). Note that Rac1-deficient cells (K/K) had decreased ability to contract a collagen gel matrix (*P < 0.05) as compared with wild-type (C/C) fibroblasts and that addition of H2O2 to Rac1-deficient cells (K/K) restored this ability (*P < 0.05, Student’s t-test).