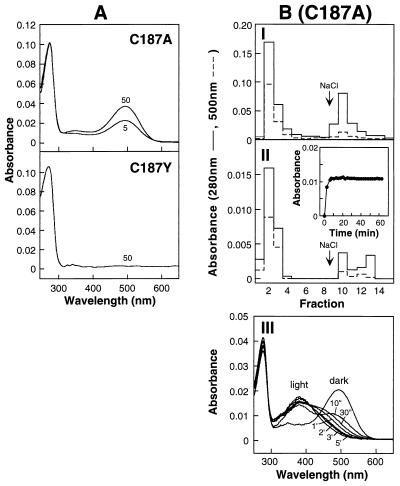
Figure 4.
Characterization of the mutant rhodopsin, formed from expressed opsin C187A, and opsin C187Y. (A) UV–vis absorption spectra of products after treatment of COS-1 cells with 11-cis-retinal at concentrations of 5 μM and 50 μM (C187A) and 50 μM (C187Y). Elution from 1D4-Sepharose column was with Buffer A containing 0.05%DM plus 100 μM peptide. (BI) Elution profile from 1D4-Sepharose of the in vivo-treated (50 μM) C187A. Elution of the first eight fractions (300 μl) was with Buffer J; the following seven fractions were with Buffer K containing salt. II. Elution profile from 1D4-Sepharose of the in vitro-treated (33.3 μM) C187A opsin. As described in I, the first eight fractions (300 μl) were eluted with Buffer J; the following seven fractions were with Buffer K containing salt. The procedure for retinal binding in vitro of the C187A opsin (Inset) was as described (20). III. Bleaching behavior for the second fraction eluted with Buffer J (no salt) in I. The dark UV–vis spectrum shown had an A280/A500 ratio of 1.7.