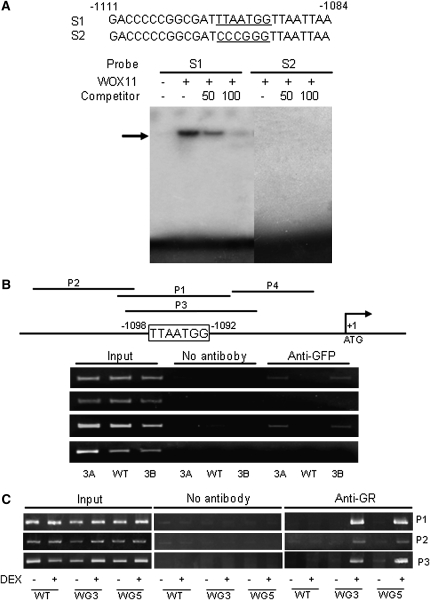
Figure 9.
WOX11 Interacts with the RR2 Gene in Vitro and in Vivo.
(A) Gel shift assays of WOX11 protein binding to a promoter sequence (S1) of RR2 containing the WOX binding site (underlined) or a mutant version of the promoter (S2). E. coli–produced WOX11 protein was incubated with 32P-labeled S1 or S2 in the absence or presence of 50 or 100 M excess of the corresponding cold probes and analyzed by electrophoresis. The shifted band is indicated by an arrow.
(B) ChIP analysis of transgenic plants expressing a WOX11-GFP fusion protein. Nuclei from two WOX11-GFP expression lines (3A and 3B) and the wild-type plants were immunoprecipitated by anti-GFP or without antibody. The precipitated chromatin fragments were analyzed by 26 cycles of PCR using four primer sets (P1 to P4) amplifying four RR2 promoter regions as indicated. The relative nucleotide positions of the putative WOX binding site are indicated (with the initiation ATG codon assessed as +1). One-tenth of the input chromatin was analyzed as controls.
(C) ChIP analysis of WOX11-GR transgenic plants using antibodies against mouse glucocorticoid receptor. Nuclei from two WOX11-GR expression lines (WG3 and WG5) and wild-type plants treated with (+) or without (–) DEX were immunoprecipitated by anti-GR or without antibody. The precipitated chromatin fragments were analyzed by 28 cycles of PCR using three primer sets (P1 to P3) as indicated. One-tenth of the input chromatin was analyzed as controls.