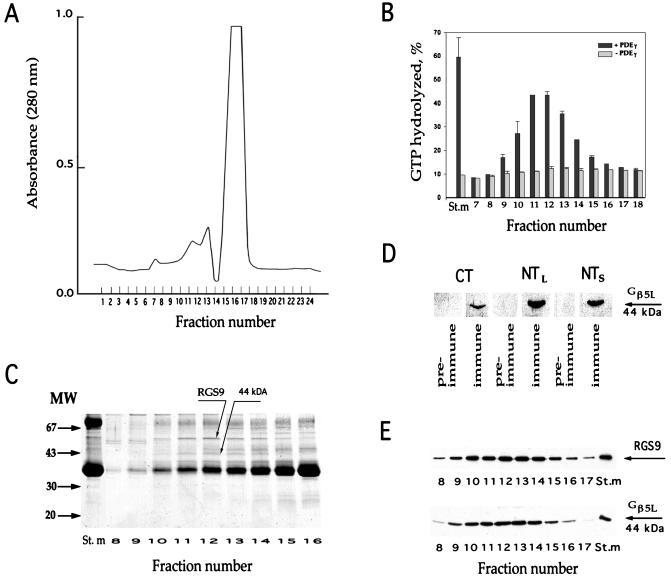
Figure 1.
Comigration of RGS9 and Gβ5L during gel filtration. Washed ROS membranes (containing 3 mg rhodopsin) were solubilized in 400 μl of buffer (20 mM Hepes adjusted to pH 7.4 by KOH, 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, and 2% lauryl sucrose) and loaded on the Superose 6 column attached to the fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) system (Pharmacia). The column was equilibrated by the same buffer containing 0.5% lauryl sucrose, 5% glycerol, and 2 mg/ml soybean l-α-phosphatidylcholine (Sigma product P-5638). The elution rate was 0.4 ml/min; the fraction size was 0.4 ml. (A) Protein elution profile monitored at 280 nm. The major source of the UV absorbance is rhodopsin. (B) GAP activity of RGS9 in chromatography fractions. Single-turnover transducin GTPase measurements were performed in duplicate with and without PDEγ (see Materials and Methods). The y-axis value represents the percentage of GTP hydrolysis over the 5-s period; error bars indicate the range of determined values. The St.m bars represent the activity in the starting material after it was diluted to achieve the same lauryl sucrose, glycerol, and phosphatidylcholine concentration as in the fractions. (C) Coomassie staining of proteins in fractions surrounding the peak of RGS9 activity. (D) Western blot immunostaining of the 44-kDa protein band by three immune and pre-immune serums raised in sheep against the Gβ5L C-terminal peptide (CT), Gβ5L N-terminal peptide (NTL), and N-terminal peptide of the Gβ5 short splice variant (NTS). (E) Comigration of RGS9 and Gβ5L in the chromatography fractions. Western blots were probed with rabbit anti-RGS9c and anti-NTS antibodies.