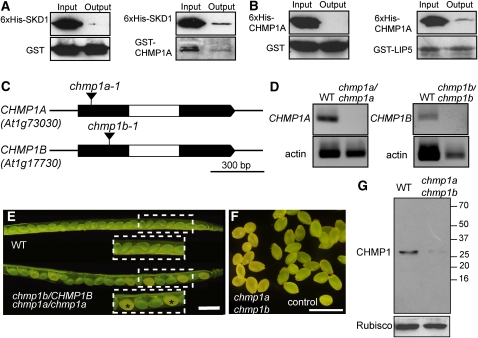
Figure 2.
Interaction Analysis between CHMP1 and ESCRT-Related Proteins and Characterization of Arabidopsis chmp1 Mutant Alleles.
(A) and (B) In vitro pull-down assays confirmed the interaction between CHMP1A and SKD1 (A) and CHMP1A and LIP5 (B). Protein gel blots of in vitro glutathione agarose pull-down show that 6xHis tagged At-SKD1 interacts with GST-At-CHMP1A but not with GST alone and 6xHis tagged At-CHMP1a interacts with GST-At-LIP5 but not with GST alone. All the recombinant proteins were detected using either anti-GST (bottom panels) or anti-His (top panels) antibodies.
(C) Schematic representation of distribution of exons (black) and introns (white) in CHMP1A and B. Inverted wedges indicate the T-DNA insertions in the first exon of CHMP1A and CHMP1B.
(D) RT-PCR from RNA extracts of the chmp1a and chmp1b single mutants. Two biological replicates were performed.
(E) Seeds from wild-type and chmp1a/CHMP1A chmp1b/chmp1b plants. Asterisks indicate double mutant seeds.
(F) Detail of seeds dissected from one single mutant silique showing double mutant and wild type–looking (control) seeds containing two or more chmp1 mutant alelles.
(G) Protein gel blot of total protein extracts from wild-type and chmp1a chmp1b mutant embryos. CHMP1 proteins were detected with a polyclonal antibody raised against the full-length maize SAL1/CHMP1 protein (Tian et al., 2007). Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) was used as loading control.
Bars = 1 mm.