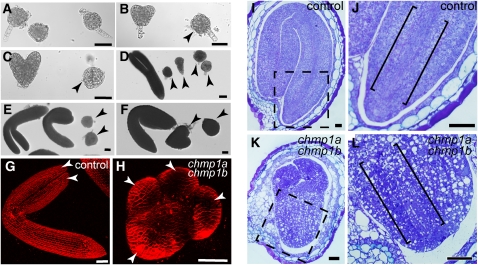
Figure 3.
Phenotypic Analysis of chmp1a chmp1b Double Mutant Embryos and Seeds.
(A) to (F) Developmental stages of dissected embryos from chmp1a/chmp1a CHMP1B/chmp1b plants. Wild type–looking embryos shown on the left side and double mutant embryos (arrowheads) on the right side of panels.
(G) and (H) Confocal images of control and mutant embryos. The mutant embryo is seen from a top view showing the presence of four rudimentary cotyledons (arrowheads).
(I) to (L) Longitudinal sections of seeds produced by chmp1a/chmp1a CHMP1B/chmp1b plants.
(I) and (J) Wild type–looking seed used as control.
(J) Detail of the root and procambial strand (indicated by brackets) of the embryo shown in (I).
(K) and (L) chmp1a chmp1b double mutant embryo.
(L) Detail of the root pole of the mutant embryo shown in (K). Note the excentrically located procambial strand (indicated by brackets).
Bars = 50 μm.