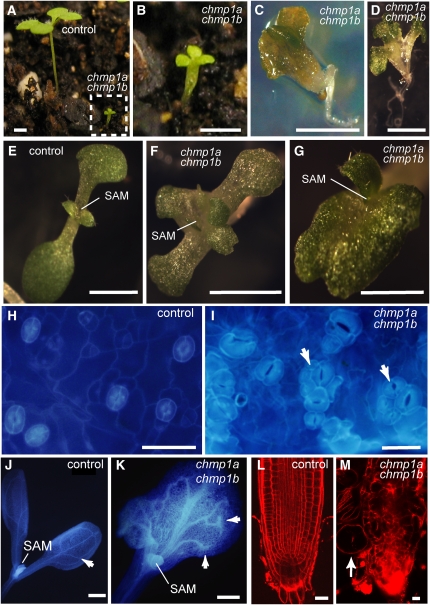
Figure 4.
Phenotype of chmp1a chmp1b Double Mutant Seedlings.
(A) to (G) Seedlings derived from chmp1a/chmp1a CHMP1B/chmp1b plants. Note multiple cotyledons of mutant seedlings in (B) to (D).
(E) to (G) Shoot apical regions in control (E) and chmp1a chmp1b mutant seedlings ([F] and [G]).
(H) and (I) Cotyledons stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole showing the distribution of stomata in control (H) and mutant seedlings (I). Note the clustered stomata in mutant cotyeldons (arrows in [I]).
(J) and (K) Seedlings stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole showing the venation pattern in cotyledons. Whereas the lateral veins in the control seedlings are fused close to the cotyledon margin (arrow in [J]), lateral veins in the mutant cotyledons end freely (arrows in [K]). SAM, shoot apical meristem.
(L) and (M) Root architecture in control (L) and chmp1a chmp1b mutant seedlings (M) stained with propidium iodide. Note the enlarged root epidermal cells in the mutant (arrow).
Bars = 5 mm in (A) to (D), 2 mm in (E) to (G), 50 μm in (H) and (I), 500 μm in (J) and (K), and 20 μm in (L) and (M).