Figure 5.
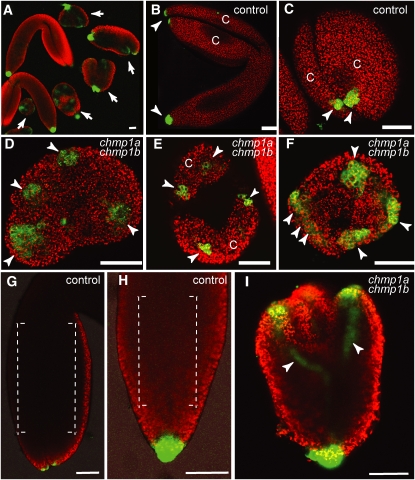
DR5revpro:GFP Expression in Control and chmp1a chmp1b Mutant Embryos.
(A) Overview of wild type–looking (control) and chmp1a chmp1b mutant embryos (arrows) expressing the DR5revpro:GFP reporter. Chlorophyll autofluorescence (red) was used to visualize the embryos.
(B) and (C) Control mature embryos. GFP signal (arrowheads) was detected in the tips of cotyledons (C) and in the root pole. (C) shows detail of apical view of cotyledon.
(D) to (F) Optical cross sections through the apical region of double mutant embryos showing GFP signal (arrowheads) in the tip of rudimentary cotyledons (C).
(G) and (H) Wild-type embryos with undetectable GFP signal in the procambial strand region (brackets) of cotyledons (G) and axis (H).
(I) Double mutant embryo showing strong GFP signal in procambial strands (arrowheads).
Bars = 50 μm.