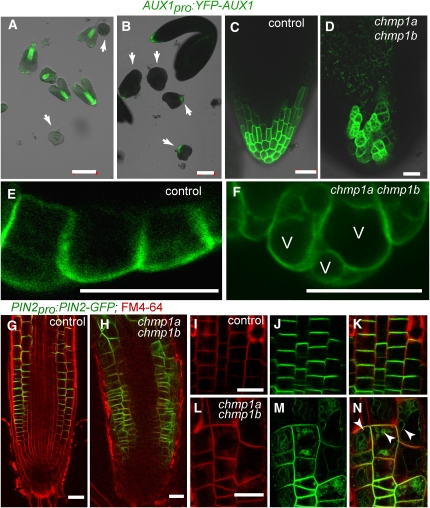
Figure 9.
Expression Pattern and Subcellular Localization of AUX1-YFP and PIN2-GFP in Control and chmp1a chmp1b Mutant Embryos.
(A) and (B) Superimposed transmission and confocal images of control and chmp1a chmp1b mutant embryos expressing AUX1pro:AUX1-YFP.
(A) Control embryos at the early torpedo stage expressed AUX1-YFP at the procambial strand and root pole, whereas the chmp1a chmp1b mutant embryos (arrows) do not express detectable levels of AUX1-GFP.
(B) Mature control and chmp1a chmp1b mutant embryos expressing AUX1-YFP at the root pole.
(C) and (D) Detail of control and chmp1a chmp1b mutant roots expressing AUX1-YFP.
(E) and (F) Control and chmp1a chmp1b embryo cells expressing AUX1-YFP at the root pole. Note the AUX1-YFP signal from the vacuolar membrane in mutant cells. V, vacuole.
(G) to (N) Expression of PIN2-GFP in epidermal and cortical cells in roots of control and chmp1a chmp1b mutant seedlings stained with FM4-64.
(I) to (K) Polarized localization of PIN2-GFP in the plasma membrane of epidermal cells in control roots.
(L) to (N) Localization of PIN2-GFP in chmp1a chmp1b root epidermal cells. Note the partial loss of polarized localization and the strong PIN2-GFP signal from vacuolar membranes (arrowheads).
Bars = 100 μm in (A) and (B) and 20 μm in (C) to (N).