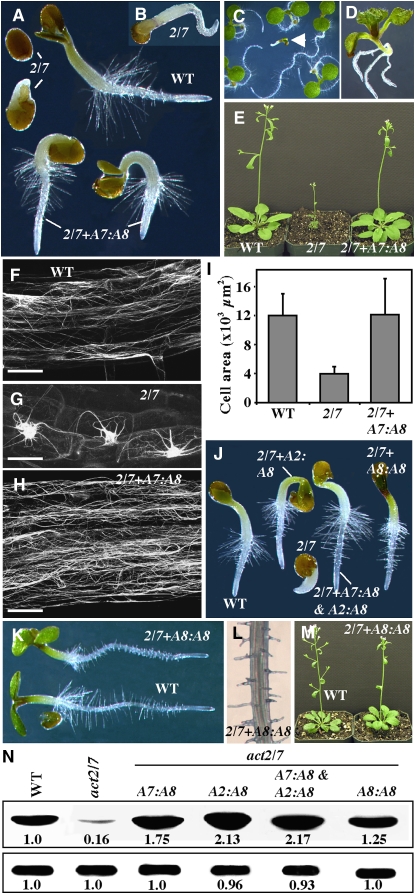
Figure 12.
Suppression of act2-1 act7-4 Double Mutant Phenotypes by Overexpression of ACT8.
(A) Germinating seedlings (36 h old) of wild-type, act2-1 act7-4 (2/7), and act2-1 act7-4 double mutants complemented with A7P:A8 (2/7+A7:A8).
(B) Six-day-old act2-1 act7-4 seedling.
(C) Segregation of F3 act2-1 act7-4 plants complemented with the A7P:A8 transgene. Arrowhead points to a seedling that lost the transgene.
(D) Sixteen-day-old seedling indicated in (C).
(E) Thirty-day-old plants. Normal growth is seen in the act2-1 act7-4 mutant overexpressing ACT8 from ACT7 regulatory sequences.
(F) to (H) Actin filament organization in the wild type, act2-1 act7-4 double mutant, and the rescued plant (2/7+A7:A8), all expressing GFP-fABD2. Bars = 50 μm.
(I) Restoration of leaf epidermal cell size to wild-type sizes in act2-1 act7-4 plants complemented with A7P:A8 (n = 30). The error bars represent sd.
(J) Seedlings (36 h old) showing full or partial rescue of the act2-1 act7-4 double mutant phenotype by overexpression of ACT8 from ACT2 (A2:A8), ACT8 (A8:A8), and ACT7 and ACT2 (A7:A8 and A2:A8) regulatory sequences.
(K) to (M) Phenotypes of act2-1 act7-4 plants complemented with A8P:A8.
(K) Four-day-old seedlings.
(L) Root.
(M) Five-week-old plants.
(N) Protein gel blot analysis of total actin expression in the wild type, act2-1 act7-4 double mutant, and different rescued plants (top row). PEPC levels are shown in the bottom row. The numbers at the bottom of the blots indicate the relative levels of respective proteins.