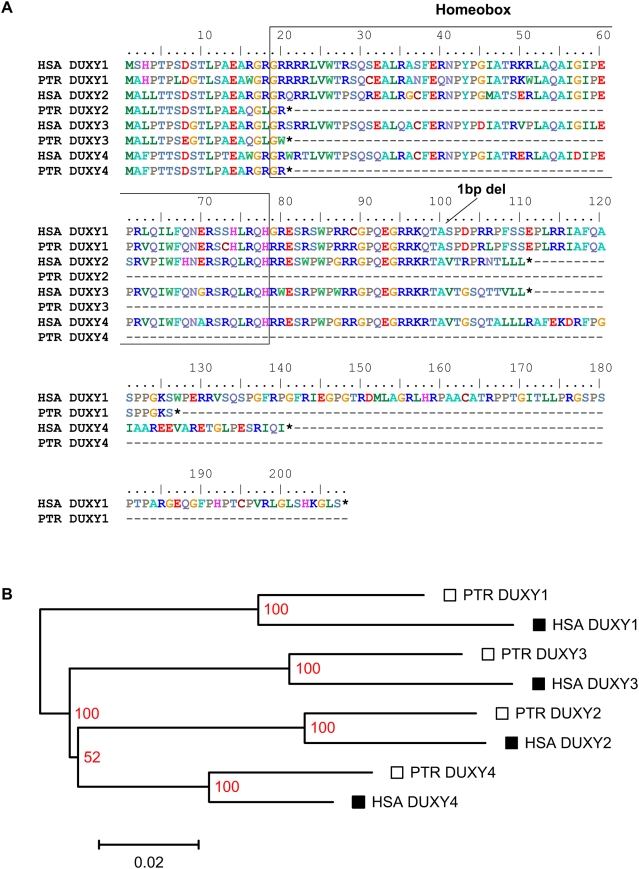
Figure 5. Amino acid sequence comparison and phylogenetic relationships of human and chimpanzee DUXY copies.
(A) Comparison of the predicted amino acid sequence of orthologous human (HSA DUXY1–4) and chimpanzee (PTR DUXY1–4) Y-chromosomal DUX copies. The colour code corresponds to the CLUSTALW default for amino acid sequence alignments. Analogous to the human DUXY genes, none of their chimpanzee counterparts contain a second homeodomain. The 1-bp deletion previously identified in HSA DUXY1 is also present in PTR DUXY1, the only chimpanzee DUXY gene copy presumably capable to encode a functional protein. The chimpanzee DUXY copies DUXY2–4 carry a stop codon at position 21 of the putative DUXY open reading frame. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of DUXY gene copies of human and chimpanzee. The gene phylogeny is based on a molecular phylogenetic analysis using maximum likelihood methods. Topology and branch lengths were generated with TreeView. Each branch termini is labeled with the abbreviation of the corresponding DUX gene copy. The bootstrap value is positioned without any spacing at the branching point (red).