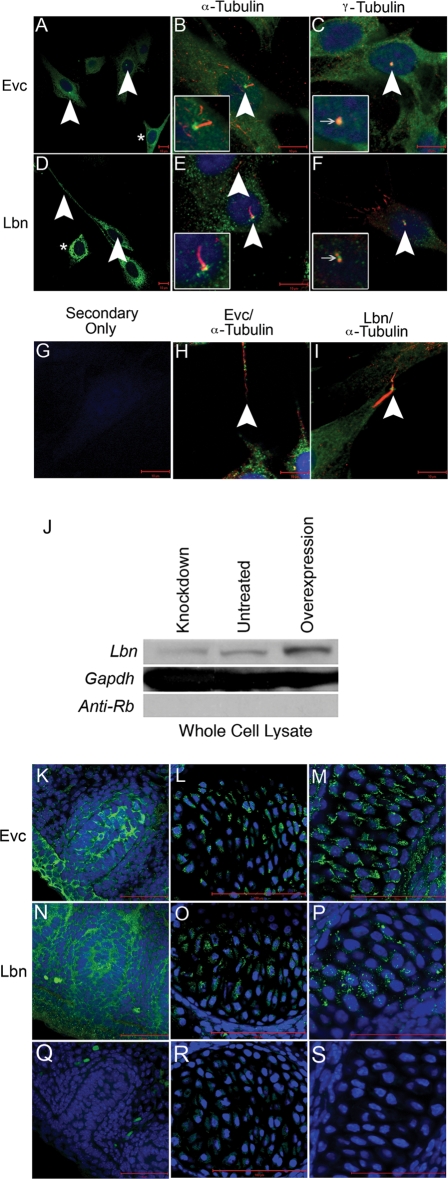
Figure 3.
Novel peptide-specific EVC antibodies confirm localization of Evc protein and co-staining with the newly generated LBN antibody reveals these proteins are expressed in overlapping structures. Expression of EVC alone (A) and co-staining with acetylated tubulin (B) or gamma tubulin (C) in NIH3T3 cells confirms antibody specificity by identification of EVC at the base of cilia. Expression of LBN alone (D) and co-staining with acetylated tubulin (E) or gamma tubulin (F) reveals an overlap of EVC and LBN protein in the cilia. Asterisks in (A and D) show protein presence in the cytoplasm of the cell outside of cilia structures. (G) serves as a negative control while (H and I) reveal the presence of EVC and LBN overlapping with acetylated tubulin-based structures that are not cilia. All scalebars in (A–I) represent 10 µM. Western blot for LBN protein (J) identified a band of the estimated size, 148 kDa. Compared with untreated cultures, the intensity of the LBN band in whole cell lysates decreased when treated with Lbn siRNA (Knockdown) and increased upon transfection with Sport6-pCMV-mLbn (Overexpression). GAPDH is used as a loading control and anti-Rb secondary antibody is a negative control for the western blot protocol. These findings confirm LBN antibody specificity. EVC antibody specificity is further confirmed in previously reported in vivo structures including the vibrissae (K), the vertebrae (L) and the cartilage primordium of the nasal bone (M) in a 15.5 dpc sagittal section of an embryo. LBN immunofluorescence reveals overlapping expression in these structures (N–P). Negative controls (Q–S) show minimal background. All scalebars in images (K–S) represent 50 µM.