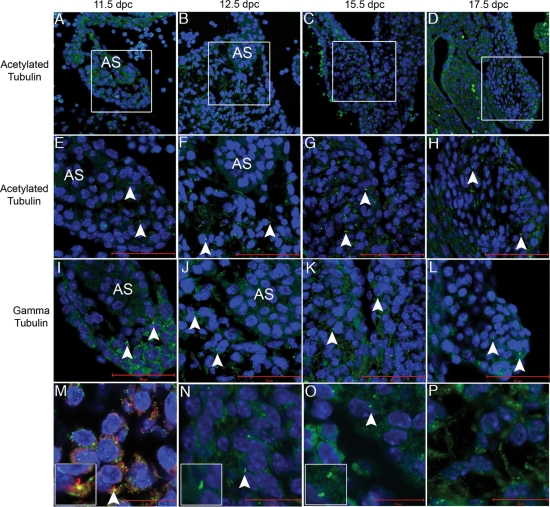
Figure 5.
Acetylated tubulin, a marker of cilia that colocalizes with EVC in cell culture, is present in the developing heart. Acetylated tubulin (seen here in green) is identified in the primary atrial septum (A,E and I), the AV junction (B,F and J) and the developing AV valves (C,D,G,H,K and L). Boxes in (A,B,C and D) indicate areas of higher magnification in (E–L). (M) displays co-staining of both acetylated and gamma tubulin confirming the presence of cilia. In images (E–N), the scale bars depict 50 µM while the scale bar represents 20 µM in (M–P). (N) is a higher magnification of acetylated tubulin revealing the cilia axonene and (O) is a higher magnification of gamma tubulin, which marks the basal bodies. (P) shows evidence of acetylated tubulin outside the cilia in mesenchymal structures of the heart. Blue Topro-3 staining marks the nuclei. Arrowheads indicate individual cilia.