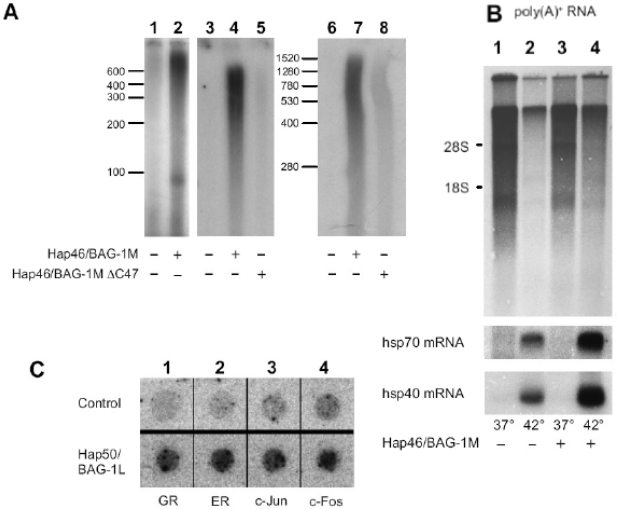
Figure 5.
Stimulation of transcription by Hap46/BAG-1M and Hap50/BAG-1L.
(A) In vitro transcription assays were carried out with HeLa nuclear extracts using either plasmid DNA (lanes 1 and 2), linearized prokaryotic DNA without a promoter (lanes 3 to 5), or eukaryotic, linear DNA without a promoter (lanes 6 to 8). Hap46/BAG-1M (lanes 2, 4, 7) or the carboxy terminally deletion variant Hap46/BAG-1M C47 (lanes 5 and 8) were added, as indicated. Newly synthesized radiolabeled RNA was analyzed by gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. Positions of RNA markers are shown along the margins. From ref. [15]. (B) DU145 cells were transfected with an expression vector coding for Hap46/BAG-1M (lanes 3 and 4) or not (lanes 1 and 2). As indicated, cells were then submitted to heat treatment at 42°C for 2 h. Newly synthesized radiolabeled poly(A)+RNA was analyzed by gel electrophoresis and autoradiography (upper panel). The positions of 18 S and 28 S rRNAs are shown along the margin. The same filters were subsequently used for Northern hybridization with radiolabeled cDNAs encoding hsp70 or hsp40 (lower panels). From ref. [13]. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with an expression vector coding for Hap50/BAG-1L (lower panel) or not (upper panel) and used for nuclear runoff transcription assays. Newly synthesized radiolabeled RNAs were probed with dot-blotted cDNAs encoding the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), the estrogen receptor (ER), c-Jun, or c-Fos, as indicated. Detection was by autoradiography. From ref.[14].