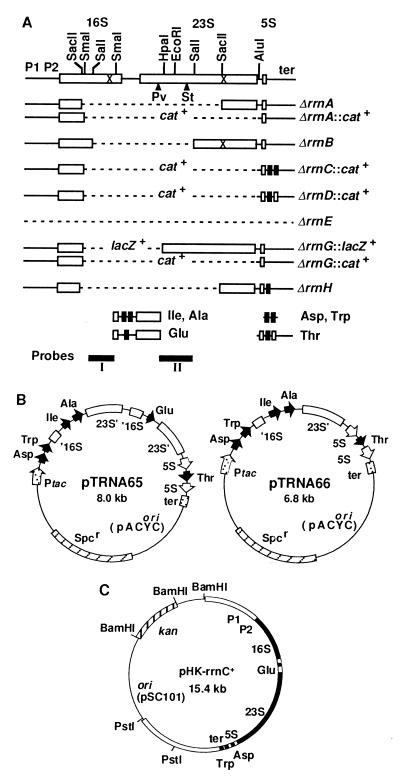
Figure 1.
(A) Deletion mutations introduced into the chromosome. Open and filled rectangles are rRNA and tRNA genes, respectively. Deleted regions are shown by broken lines. cat+ and lacZ+ indicate the deleted regions are replaced with the coding regions of these genes. The rRNA promoters (P1P2) and terminators (ter) also are shown. The crosses in the 16S and 23S rRNA genes indicate the positions of the Spc and erythromycin resistance mutations, respectively. ▴ indicates the position of an intervening sequence in the 23S rRNA gene of S. typhimurium (St) or P. vulgaris (Pv). The four DNA fragments with tRNA genes cloned in pTRNA65 are shown below the rRNA operons. (B) pTRNA plasmids. Relative positions and orientation of the tac promoter, tRNA genes and the 5S rRNA gene are indicated by arrows. The rRNA transcription terminators and the truncated 16S and 23S rRNA genes also are shown. Truncation of the genes is indicated by a prime. The plasmids are not drawn to scale. (C) An rRNA plasmid carrying the wt rrnC operon. Filled and open boxes indicate stable RNA genes and their flanking sequences, respectively. The size of the BamHI–PstI fragment containing the rrnC operon is 8.4 kb.