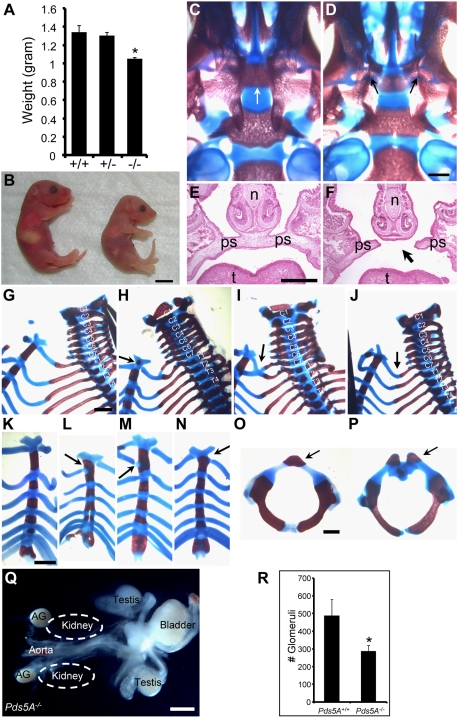
Figure 1. Pds5A deficiency results in growth retardation, abnormal skeletal patterning and cleft palate.
(A) The weight of Pds5A−/− P0 mice is significantly lower than that of wildtype and heterozygous littermates (WT, n = 8; Pds5A+/−, n = 30; Pds5A−/−, n = 39). Error bars represent s.e.m. * P<0.001, Student's unpaired, two tailed t-test. (B) Morphology of wildtype and Pds5A mutant mice. Note that newborn Pds5A−/− pups (right) were smaller than their wildtype littermates (left). Note too the absence of milk in the stomach of the Pds5A−/− pup. Scale bar: 0.5 cm. (C, D) Alizarin Red S and Alcian Blue staining of neonatal skulls demonstrates complete cleft palate (arrows) of a Pds5A−/− neonate (D) compared with the proximity of palatal bones in the midline (arrow) in the wildtype control (C). Scale bar: 0.5 mm. (E, F) Palatogenesis defects illustrated using H&E stained coronal sections of E18.5 wildtype (E) and Pds5A−/− (F) embryos. ps, palatal shelf; n, nasal bone; t, tongue. Arrows in F point to the unfused palatal shelves. Scale bar: 1 mm. (G–P) Alizarin Red S and Alcian Blue staining of newborn skeleton. Bone is stained red and cartilage is stained blue. (G–J) Cervical and thoracic vertebrae and ribs. Note the C7-T1 fusions (arrows in H, I) and cervical rib (arrow in J) in Pds5A−/− mice, compared to the normal skeletal patterning in wildtype animals (G). Cervical (C) and Thoracic (T) vertebrae are marked by numbers. (K–N) Sternum morphology. Arrows denote ectopic rib-sternum conjunctions (L–N) in Pds5A−/− mice compared to sternum patterning in wildtype (K). (O, P) Morphology of the first cervical vertebrae. Note the unfused ossification centers at the dorsal tip of the first cervical vertebrae (arrows) in Pds5A−/− animal (P) compared to wildtype (O). Scale bar for G–N: 1 mm; scale bar for O–P: 0.5 mm. (Q, R) Renal abnormalities in neonatal Pds5A-deficient mice. (Q) Bilateral renal agenesis in Pds5A−/− newborn animals. AG, adrenal gland. Scale bar: 1 mm. (R) The total number of glomeruli in kidneys from P0 Pds5A−/− and wildtype mice were counted (n = 4 animals, 8 kidneys). (*, P<0.05, student unpaired t test; mean±s.e.m.).